UE反射系统实现解析
原文出处:UE反射系统实现解析
丨 导语 反射系统作为游戏引擎的基础能力,在游戏开发中扮演着至关重要的角色,它能够支持运行时获取对象的类型信息,以及动态调用对象的属性和方法。本文中,我们将详细解析UE反射系统的代码实现,帮助大家更有效地了解UE的反射机制。
1.概念介绍
1982 年 MIT 的 Smith, Brian Cantwell 在他的博士论文中最早提出了程序反射的概念:
既然我们可以构造“有关某个外部世界表示”的计算过程, 并通过它来对那个外部世界进行推理; 那么我们也可以构造能够对自身表示和计算进行推理的计算过程,它包含负责管理有关自身的操作和结构表示的内部过程。
编程语言中的反射是指在运行时检查、访问和修改程序的结构、状态和行为的能力。
它允许程序在运行时动态地获取和操作类型、对象、方法和属性等信息,而不需要在编译时提前知道这些信息。
一般情况下,针对面向对象语言,反射系统需要提供的基础能力大致包含:
创建实例
- 根据类名,创建类对象实例
访问成员变量
根据类名,访问所有成员变量的meta数据:名字、类型等
根据类名与成员名字,访问/修改某类对象的成员变量数据
调用成员函数
- 根据类名,访问所有成员函数的meta数据:名字、参数信息,返回值信息等
- 根据类名与函数名字,调用某类对象的成员函数
2.piccolo反射系统实现
在真正介绍UE反射实现前,我们先解析另外一款游戏引擎(piccolo)的反射系统实现,既为开拓视野,更旨在建立一个最简单通透的反射系统实现认知。
2.1.piccolo引擎介绍
piccolo引擎是一款开源mini版游戏引擎,专为【GAMES104(现代游戏引擎入门必修课)】课程打造。该引擎的实现宗旨为:提取最简单精炼的思路,实现现代游戏引擎的各类基础功能。
2.1.piccolo反射系统实现概览
简单了解下piccolo反射系统的总体实现:
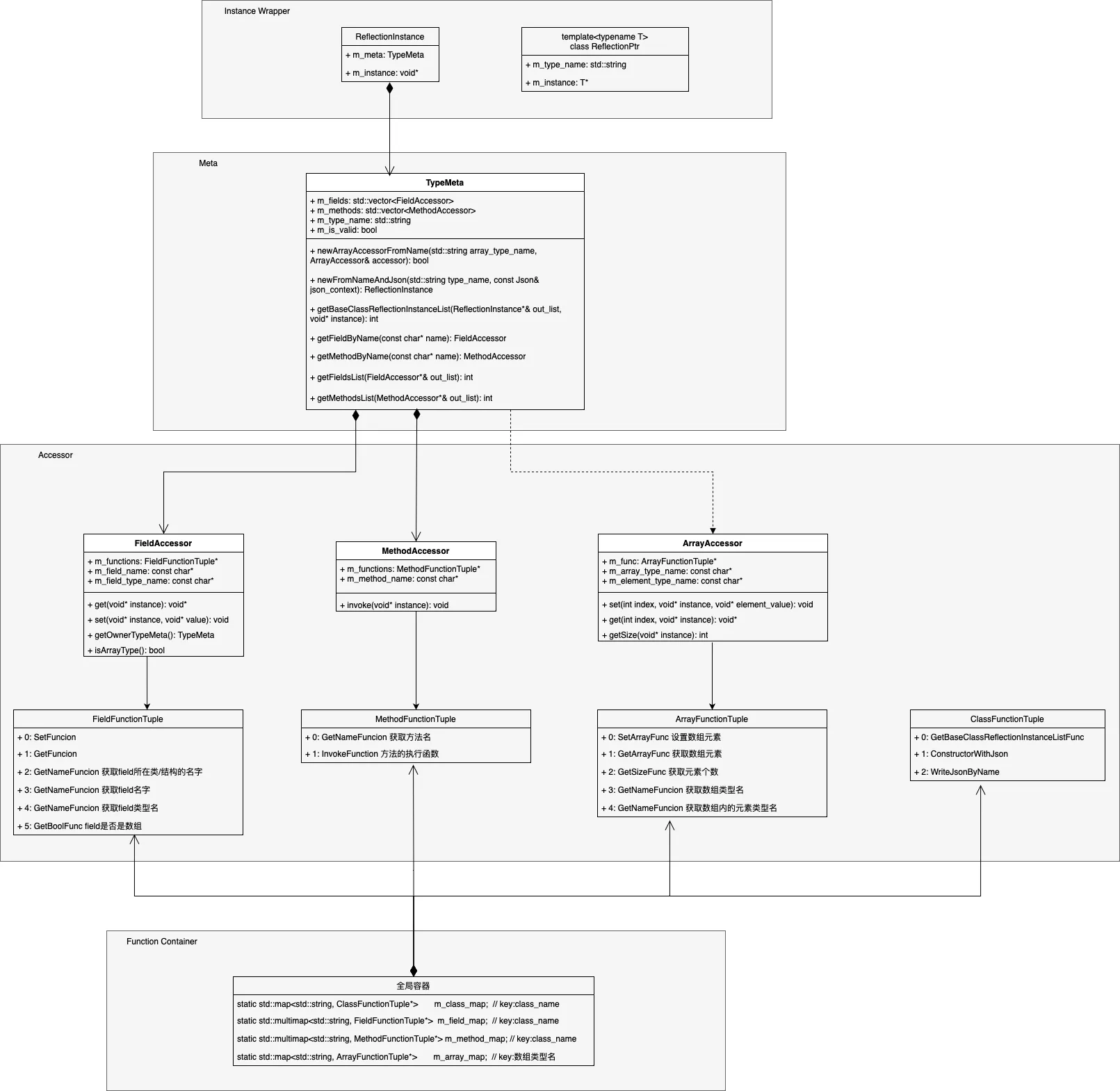
通过上图可以看出:
- piccolo反射实现多用组合关系,基本不使用派生关系,整体实现清晰有序。
- piccolo反射实现中有着明显的四层结构划分,分别为:
- Instance Wrapper层:对于类对象的访问包装,不用过多关注。
- Type Meta层:为class结构定义的Meta数据结构,内部包含了class结构中所有fields与methods的accessor。
- Accessor层:为class、array、field、mothod定义的操作处理器数据结构。
- Function Container层:全局容器,用于存储class、array、field、mothod的操作处理器对象。
上图四层结构中,最核心部分是Accessor层,先对其进行详细介绍。
2.2.Accessor层
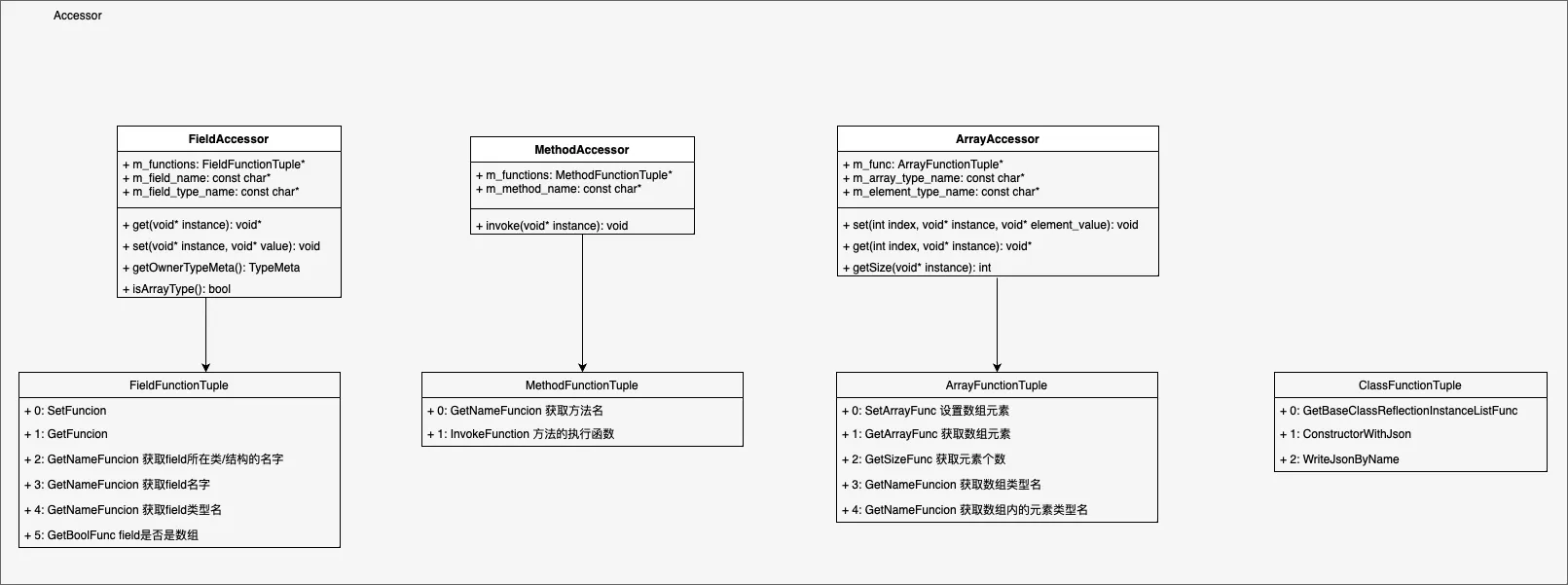
该层中最关键的部分是**FunctionTuple定义:
2.2.1.ClassFunctionTuple
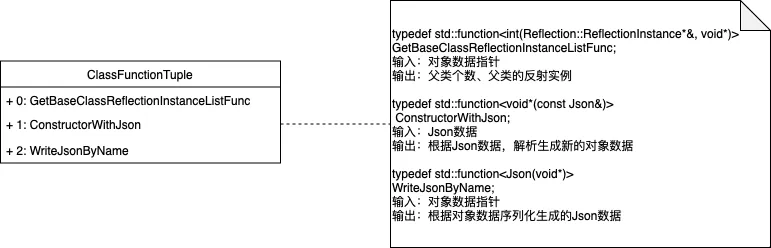
为Class提供能力:
解析class的派生关系
对类对象执行序列化与反序列化
2.2.2.ArrayFunctionTuple
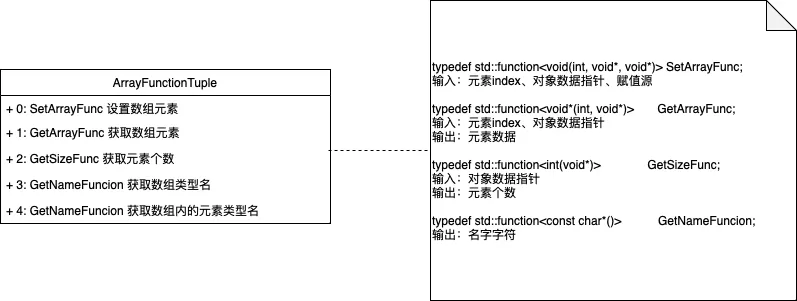
为Array提供能力:
Get/Set Array元素内存数据
获取Array Size
获取Array的Meta数据:数组类型名、数组元素的类型名
示例std::vector
数组类型名:std::vector
数组元素的类型名:int
注:可以将Array看做一种特殊的Class,std::vector
2.2.3.FieldFunctionTuple
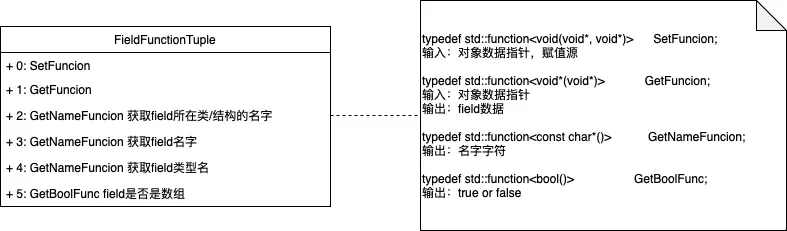
为Field提供能力:
Get/Set Field的内存数据
获取Field的Meta数据:名字、类型、是否是数组、所在Class的名字
2.2.4.MethodFunctionTuple
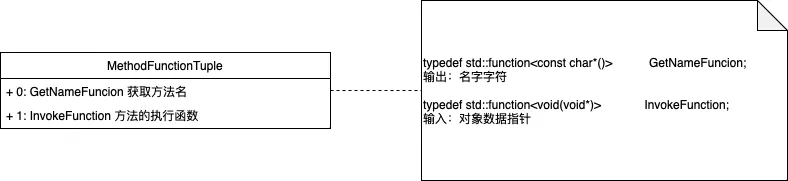
为Method提供能力:
- Method调用
注:piccolo拥有一定的demo性质,只支持无传参无返回的方法反射。
2.2.5.示例
class XibaTest
{
public:
void test() {m_int = 1;}
public:
int m_int;
float m_float;
std::vector<int> m_int_array;
};
对上述class创建反射数据,需要生成如下对象:
一个ClassFunctionTuple对象,内部包含XibaTest的基类获取接口、序列化与反序列化接口
一个ArrayFunctionTuple对象,内部包含std::vector
类型数组的元素访问接口 三个FieldFunctionTuple对象
a. FieldFunctionTuple对象for
XibaTest::m_int,内部包含m_int成员访问接口b. FieldFunctionTuple对象for
XibaTest::m_float,内部包含m_float成员访问接口c. FieldFunctionTuple对象for
XibaTest::m_int_array,内部包含m_int_array成员访问接口一个MethodFunctionTuple对象,内部包含XibaTest::test()的invoke接口
通过上述的FunctionTuple对象,传入对象指针后,便能够实现对象成员的访问与对象函数的调用。
但此时还缺少对FunctionTuple对象的组织与管理,即如何通过class_name获取到为对应class创建的FunctionTuple对象集合。
此时便需要用到Function Container层提供的数据管理功能。
2.3.Function Container层
该层通过创建全局容器,用于维护所有FunctionTuple对象:
static std::map<std::string, ClassFunctionTuple*> m_class_map; // key:class_name
static std::multimap<std::string, FieldFunctionTuple*> m_field_map; // key:class_name
static std::multimap<std::string, MethodFunctionTuple*> m_method_map; // key:class_name
static std::map<std::string, ArrayFunctionTuple*> m_array_map; // key:数组类型名
可以看出,m_class_map、m_field_map、m_method_map都以class_name作为key。
于是已知class_name后,便能够获取为该class创建的FunctionTuple集合,也即支持了通过class_name生成该class的Meta数据(也即TypeMeta)。
2.4.Type Meta层
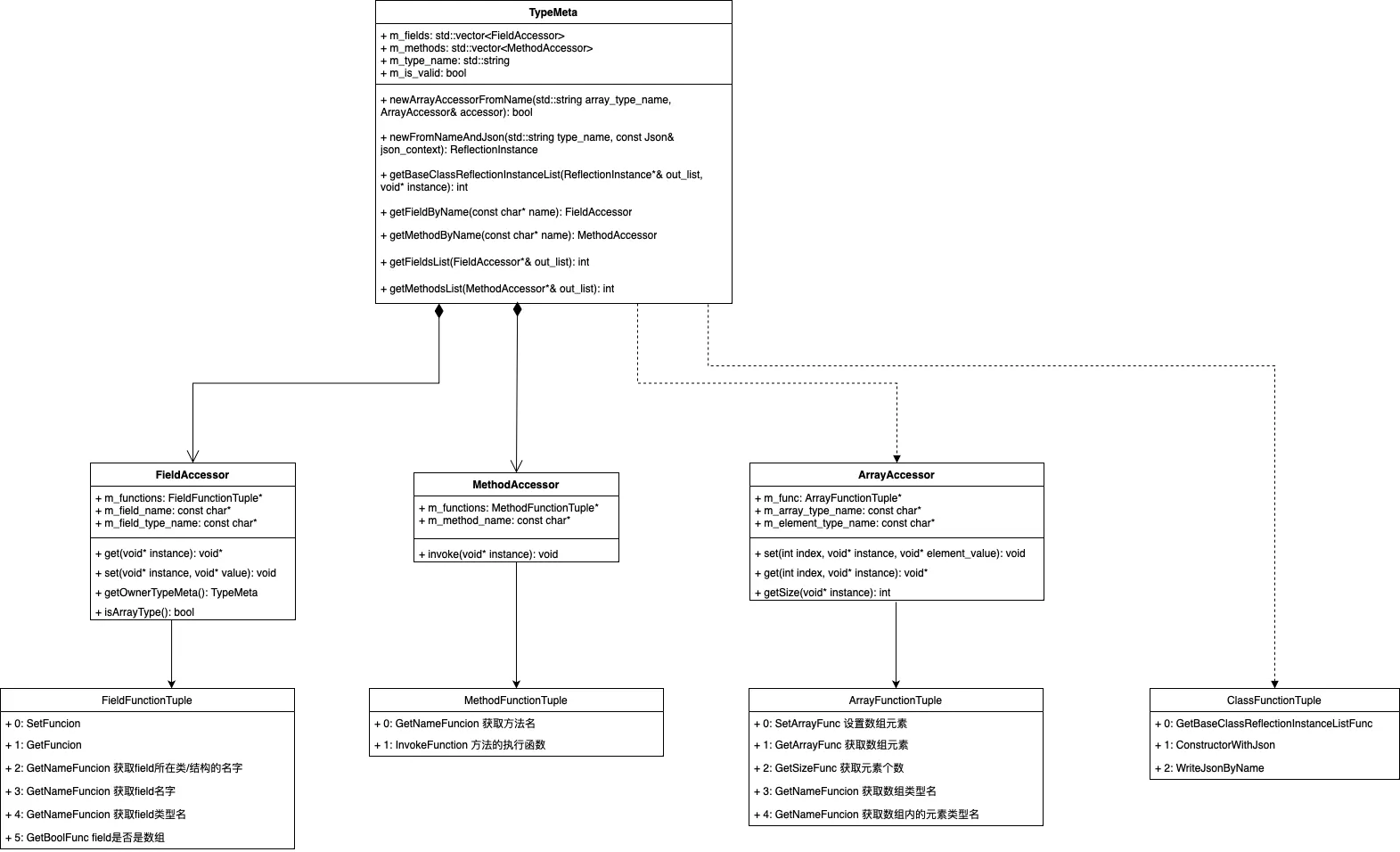
通过TypeMeta对象,便实现了反射所需的基础能力:
创建实例
访问成员变量
调用成员函数
2.5.反射信息生成示例
现在我们通过实例来查看具体的FunctionTuple创建与注册流程。
// class示例:XibaTest 内部所有fields与methods都需要创建functionTuple
CLASS(XibaTest, Methods, Fields)
{
REFLECTION_BODY(XibaTest);
public:
void test() {m_int = 1;}
public:
int m_int;
float m_float;
std::vector<int> m_int_array;
};
piccolo专门实现了meta_parse工具,用于自动生成反射信息创建&注册逻辑。
创建专属Operator类(以下代码全部由meta_parse工具自动生成):
// 为XibaTest创建专属Operator类,内部定义的接口全部为static
class TypeXibaTestOperator{
public:
static const char* getClassName(){ return "XibaTest";}
// 实现序列化与反序列化
static void* constructorWithJson(const Json& json_context){
XibaTest* ret_instance= new XibaTest;
Serializer::read(json_context, *ret_instance);
return ret_instance;
}
static Json writeByName(void* instance){
return Serializer::write(*(XibaTest*)instance);
}
// 获取基类数组
static int getXibaTestBaseClassReflectionInstanceList(ReflectionInstance* &out_list, void* instance){
int count = 0;
return count;
}
// op function for field:m_int
static const char* getFieldName_m_int(){ return "m_int";}
static const char* getFieldTypeName_m_int(){ return "int";}
static void set_m_int(void* instance, void* field_value){ static_cast<XibaTest*>(instance)->m_int = *static_cast<int*>(field_value);}
static void* get_m_int(void* instance){ return static_cast<void*>(&(static_cast<XibaTest*>(instance)->m_int));}
static bool isArray_m_int(){ return false; }
// op function for field:m_float
……
// op function for field:m_int_array
……
static bool isArray_m_int_array(){ return true; }
// op function for method:test
static const char* getMethodName_test(){ return "test";}
static void invoke_test(void * instance){static_cast<XibaTest*>(instance)->test();}
};
#ifndef ArraystdSSvectorLintROperatorMACRO
#define ArraystdSSvectorLintROperatorMACRO
// 为std::vector<int>创建专属Operator类,内部定义的接口全部为static
class ArraystdSSvectorLintROperator{
public:
static const char* getArrayTypeName(){ return "std::vector<int>";}
static const char* getElementTypeName(){ return "int";}
static int getSize(void* instance){
//todo: should check validation
return static_cast<int>(static_cast<std::vector<int>*>(instance)->size());
}
static void* get(int index,void* instance){
//todo: should check validation
return static_cast<void*>(&((*static_cast<std::vector<int>*>(instance))[index]));
}
static void set(int index, void* instance, void* element_value){
//todo: should check validation
(*static_cast<std::vector<int>*>(instance))[index] = *static_cast<int*>(element_value);
}
};
#endif //ArraystdSSvectorLintROperator
FunctionTuple的生成与注册(以下代码全部由meta_parse工具自动生成):
void TypeWrapperRegister_XibaTest(){
// 创建FieldFunctionTuple for field:m_int
FieldFunctionTuple* field_function_tuple_m_int=new FieldFunctionTuple(
&TypeFieldReflectionOparator::TypeXibaTestOperator::set_m_int,
&TypeFieldReflectionOparator::TypeXibaTestOperator::get_m_int,
&TypeFieldReflectionOparator::TypeXibaTestOperator::getClassName,
&TypeFieldReflectionOparator::TypeXibaTestOperator::getFieldName_m_int,
&TypeFieldReflectionOparator::TypeXibaTestOperator::getFieldTypeName_m_int,
&TypeFieldReflectionOparator::TypeXibaTestOperator::isArray_m_int);
// 将刚创建的FieldFunctionTuple对象注册进入全局field容器
REGISTER_FIELD_TO_MAP("XibaTest", field_function_tuple_m_int);
// 创建FieldFunctionTuple for field:m_float
// 将刚创建的FieldFunctionTuple对象注册进入全局field容器
……
// 创建FieldFunctionTuple for field:m_int_array
// 将刚创建的FieldFunctionTuple对象注册进入全局field容器
……
// 创建MethodFunctionTuple for method:test
MethodFunctionTuple* method_function_tuple_test=new MethodFunctionTuple(
&TypeFieldReflectionOparator::TypeXibaTestOperator::getMethodName_test,
&TypeFieldReflectionOparator::TypeXibaTestOperator::invoke_test);
// 将刚创建的FieldFunctionTuple对象注册进入全局method容器
REGISTER_Method_TO_MAP("XibaTest", method_function_tuple_test);
// 创建ArrayFunctionTuple for array:std::vector<int>
ArrayFunctionTuple* array_tuple_stdSSvectorLintR = new ArrayFunctionTuple(
&ArrayReflectionOperator::ArraystdSSvectorLintROperator::set,
&ArrayReflectionOperator::ArraystdSSvectorLintROperator::get,
&ArrayReflectionOperator::ArraystdSSvectorLintROperator::getSize,
&ArrayReflectionOperator::ArraystdSSvectorLintROperator::getArrayTypeName,
&ArrayReflectionOperator::ArraystdSSvectorLintROperator::getElementTypeName);
// 将刚创建的ArrayFunctionTuple对象注册进入全局array容器
REGISTER_ARRAY_TO_MAP("std::vector<int>", array_tuple_stdSSvectorLintR);
// 创建ClassFunctionTuple for class:XibaTest
ClassFunctionTuple* class_function_tuple_XibaTest=new ClassFunctionTuple(
&TypeFieldReflectionOparator::TypeXibaTestOperator::getXibaTestBaseClassReflectionInstanceList,
&TypeFieldReflectionOparator::TypeXibaTestOperator::constructorWithJson,
&TypeFieldReflectionOparator::TypeXibaTestOperator::writeByName);
// 将刚创建的ClassFunctionTuple对象注册进入全局class容器
REGISTER_BASE_CLASS_TO_MAP("XibaTest", class_function_tuple_XibaTest);
}
2.6.反射系统使用示例
auto meta = Reflection::TypeMeta::newMetaFromName("XibaTest");
Reflection::FieldAccessor* fields;
int fields_count = meta.getFieldsList(fields);
for(int i = 0; i < fields_count; ++i)
{
LOG_INFO("field_name:{} field_type:{}", fields[i].getFieldName(), fields[i].getFieldTypeName());
}
delete[] fields;
Reflection::MethodAccessor* methods;
size_t method_count = meta.getMethodsList(methods);
for(int i = 0; i < method_count; ++i)
{
LOG_INFO("method_name:{}", methods[i].getMethodName());
}
delete[] methods;
输出内容:
[info] field_name:m_int field_type:int
[info] field_name:m_float field_type:float
[info] field_name:m_int_array field_type:std::vector<int>
[info] method_name:test
2.7.总结
piccolo反射系统的实现呈现出了一种难得的简洁之美。
当然受限于该引擎的demo性质,其中仍然存在一些缺陷,比如不支持带参函数的反射、运行时性能差等等。然而即便整体实现并不完美,但确能让大家一窥反射机制的实现重点。
3.UE反射系统实现
3.1.前情提要
通过解析piccolo相关代码,可以总结出一个反射系统的实现需要包含如下部分:
Meta定义,包括:
Class/Struct的meta数据定义
Field的meta数据定义
Method的meta数据定义
Meta数据的管理
建立Class/Struct与Field/Method Meta数据的关联关系
建立
class_name与Class Meta数据的关联关系
那么带着这些总结,我们开始UE反射系统的解析之旅。
3.2.Struct反射实现
先创建一个最简单的struct示例:
USTRUCT()
struct FFGReflectionStructTest
{
GENERATED_USTRUCT_BODY()
UPROPERTY()
int32 TestVal= {4} ;
};
首先展开编译有效宏:GENERATED_USTRUCT_BODY,此宏定义在自动生成头文件中:generated.h
USTRUCT()
struct FFGReflectionStructTest
{
friend struct Z_Construct_UScriptStruct_FFGReflectionStructTest_Statics;
FORTUNEGAME_API static class UScriptStruct* StaticStruct(); // static获取Struct Meta数据
UPROPERTY()
int32 TestVal;
};
宏展开后的代码中定义了StaticStruct();,此接口返回UScriptStruct,也即我们所关注的Struct Meta数据。
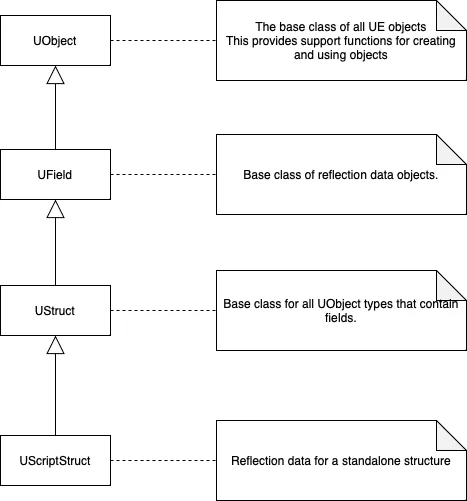
3.2.1.构造UScriptStruct
UE为构造UScriptStruct数据,定义了一套构造参数:FStructParams
struct FStructParams
{
UObject* (*OuterFunc)();// 获取struct定义所在的UObject
UScriptStruct* (*SuperFunc)();// 获取父类meta数据
void* (*StructOpsFunc)();/ 支持自定义内存结构下的动态创建与销毁struct能力,实际返回ICppStructOps*,维护有struct的size与align信息
const char* NameUTF8;// struct结构名字
SIZE_T SizeOf; // struct的size
SIZE_T AlignOf;// struct的对齐信息
const FPropertyParamsBase* const* PropertyArray;// struct内的成员变量列表,成员通过FPropertyParamsBase进行描述
int32 NumProperties;// struct内的成员变量数量
EObjectFlags ObjectFlags;// Flags describing an object instance
uint32 StructFlags; // Flags describing a struct
#if WITH_METADATA
const FMetaDataPairParam* MetaDataArray;// 其他meta信息:所在文件路径
int32 NumMetaData;
#endif
};
针对上文示例中的FFGReflectionStructTest结构,UE在自动生成的gen.cpp结构中,为FFGReflectionStructTest实例化的FStructParams对象如下:
// 为struct内的成员变量TestVal构建PropertyParams 主要信息:成员名字、成员内存偏移、成员内置类型
const UECodeGen_Private::FIntPropertyParams Z_Construct_UScriptStruct_FFGReflectionStructTest_Statics::NewProp_TestVal = {
"TestVal",
nullptr,
(EPropertyFlags)0x0010000000000000,
UECodeGen_Private::EPropertyGenFlags::Int,
RF_Public|RF_Transient|RF_MarkAsNative,
1,
nullptr,
nullptr,
STRUCT_OFFSET(FFGReflectionStructTest, TestVal),
METADATA_PARAMS(Z_Construct_UScriptStruct_FFGReflectionStructTest_Statics::NewProp_TestVal_MetaData,
UE_ARRAY_COUNT(Z_Construct_UScriptStruct_FFGReflectionStructTest_Statics::NewProp_TestVal_MetaData))
};
// struct内的成员变量列表,引用上面代码中为成员构建的PropertyParams
const UECodeGen_Private::FPropertyParamsBase* const
Z_Construct_UScriptStruct_FFGReflectionStructTest_Statics::PropPointers[] = {
(const UECodeGen_Private::FPropertyParamsBase*)&Z_Construct_UScriptStruct_FFGReflectionStructTest_Statics::NewProp_TestVal,
};
// 为Struct构建FStructParams
const UECodeGen_Private::FStructParams Z_Construct_UScriptStruct_FFGReflectionStructTest_Statics::ReturnStructParams = {
(UObject* (*)())Z_Construct_UPackage__Script_FortuneGame,// 获取struct所在的package
nullptr,// 获取父类meta数据
&NewStructOps,// 支持自定义内存结构下的动态创建与销毁struct能力,实际返回ICppStructOps*,维护有struct的size与align信息
"FGReflectionStructTest",// struct结构名字
sizeof(FFGReflectionStructTest), // struct的size
alignof(FFGReflectionStructTest), // struct的对齐信息
Z_Construct_UScriptStruct_FFGReflectionStructTest_Statics::PropPointers,// 上面代码中定义的成员变量列表
UE_ARRAY_COUNT(Z_Construct_UScriptStruct_FFGReflectionStructTest_Statics::PropPointers),// struct内的成员变量数量
RF_Public|RF_Transient|RF_MarkAsNative,// Flags describing an object instance
EStructFlags(0x00000001),// Flags describing a struct
METADATA_PARAMS(Z_Construct_UScriptStruct_FFGReflectionStructTest_Statics::Struct_MetaDataParams,
UE_ARRAY_COUNT(Z_Construct_UScriptStruct_FFGReflectionStructTest_Statics::Struct_MetaDataParams))// 其他meta信息:所在文件路径
};
具体实现中,为Struct构建Meta数据时,除了生成UScriptStruct对象,会为struct中的field生成FProperty对象。
FStructParams所包含的内容,会被赋值到各个不同的结构中:
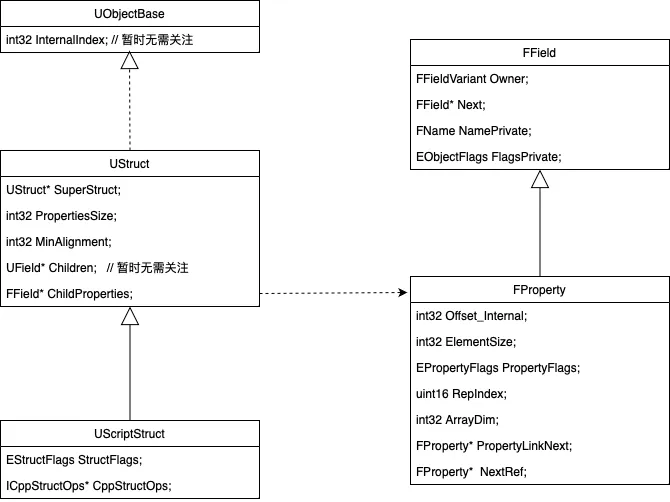
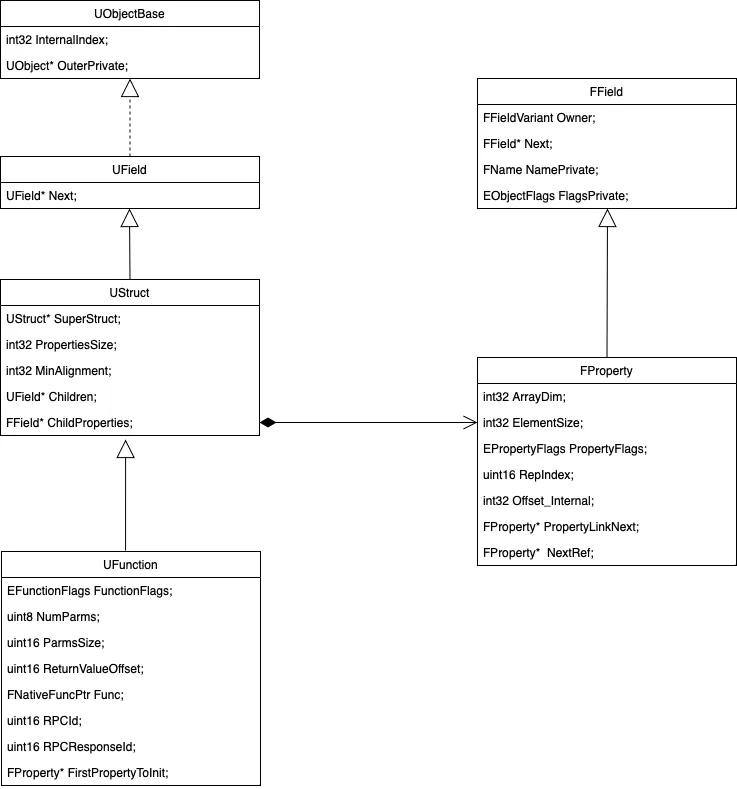
UScriptStruct结构的重要字段解析:
CppStructOps为Struct提供构造接口、序列化接口
ChildProperties维护Struct中首个field的FProperty数据指针
SuperStruct维护父结构的Meta对象指针
FProperty结构的重要字段解析:
ElementSize记录field的内存size
Offset_Internal记录field在所属类型中的地址偏移
Owner记录field的所属类型Meta数据
Next为所属类型维护下一个field的FProperty数据指针
NamePrivate记录field名字
根据UScriptStruct对象中的ChildProperties数据 与 FProperty中的Next数据,便能够拿到Struct中所有fields的FProperty数据。
另外,FProperty提供了接口ContainerPtrToValuePtr,实现功能:传入struct/class对象指针,获取到对应field的内存数据。
template<typename ValueType>
FORCEINLINE ValueType* ContainerPtrToValuePtr(void* ContainerPtr, int32 ArrayIndex = 0) const
{
return (ValueType*)ContainerVoidPtrToValuePtrInternal(ContainerPtr, ArrayIndex);
}
FORCEINLINE void* ContainerVoidPtrToValuePtrInternal(void* ContainerPtr, int32 ArrayIndex) const
{
checkf((ArrayIndex >= 0) && (ArrayIndex < ArrayDim), TEXT("Array index out of bounds: %i from an array of size %i"), ArrayIndex, ArrayDim);
check(ContainerPtr);
if (0)
{
// in the future, these checks will be tested if the property is NOT relative to a UClass
check(!GetOwner<UClass>()); // Check we are _not_ calling this on a direct child property of a UClass, you should pass in a UObject* in that case
}
// 可以看出,此处就是简单地执行了内存偏移
return (uint8*)ContainerPtr + Offset_Internal + ElementSize * ArrayIndex;
}
通过ContainerPtrToValuePtr接口,便可以方便实现对field的get/set操作。
3.2.2.注册UScriptStruct
回顾3.1的内容:
通过解析piccolo相关代码,可以总结出一个反射系统的实现需要包含如下部分:
Meta定义:Class/Struct的meta数据定义、Field的meta数据定义、Method的meta数据定义
Meta数据的管理:建立Class/Struct与Field/Method Meta数据的关联关系、建立class_name与Class Meta数据的关联关系
上文介绍了Struct的Meta定义,现在开始探索Meta数据的管理:
首先,UScriptStruct已经为内部fields维护了meta数据链表,因此不需要额外建立Struct与Field Meta数据的关联关系
因此,此节的关注重点在于:建立
struct_name与UScriptStruct数据的关联关系
3.2.2.1.全局UObject对象容器
首先介绍UE的全局容器FUObjectHashTables:
class FUObjectHashTables
{
/** Hash sets */
TBucketMap<int32> Hash; // UObject的NameHash值 -> set of UObjectBase* UScriptStruct即继承自UObjectBase
TMultiMap<int32, uint32> HashOuter; // UObject的NameHash值+UObject的拥有者指针 -> UObject的UniqueID
……
}
显而易见,将UScriptStruct注册到Hash与HashOuter中,便能够建立struct_name与UScriptStruct数据的关联关系。
另外,UE还为所有UObject维护有一个全局容器:FUObjectArray。上面提到了UObject的UniqueID便来自于该容器所提供的元素索引。
class COREUOBJECT_API FUObjectArray
{
typedef FChunkedFixedUObjectArray TUObjectArray;
/** Array of all live objects. */
TUObjectArray ObjObjects;
/** Available object indices. */
TArray<int32> ObjAvailableList;
}
FChunkedFixedUObjectArray解析
按块申请连续内存,用于存储FUObjectItem数据
对象池,不提供内存释放功能(因此上层释放FUObjectItem时,会将index存入ObjAvailableList,以供下次复用)
struct FUObjectItem
{
// Pointer to the allocated object
class UObjectBase* Object;
// Internal flags
int32 Flags;
// UObject Owner Cluster Index
int32 ClusterRootIndex;
// Weak Object Pointer Serial number associated with the object
int32 SerialNumber;
}
class FChunkedFixedUObjectArray
{
enum
{
NumElementsPerChunk = 64 * 1024,
};
/** Primary table to chunks of pointers **/
FUObjectItem** Objects;
/** If requested, a contiguous memory where all objects are allocated **/
FUObjectItem* PreAllocatedObjects;
/** Maximum number of elements **/
int32 MaxElements;
/** Number of elements we currently have **/
int32 NumElements;
/** Maximum number of chunks **/
int32 MaxChunks;
/** Number of chunks we currently have **/
int32 NumChunks;
}
FChunkedFixedUObjectArray数据结构示意:
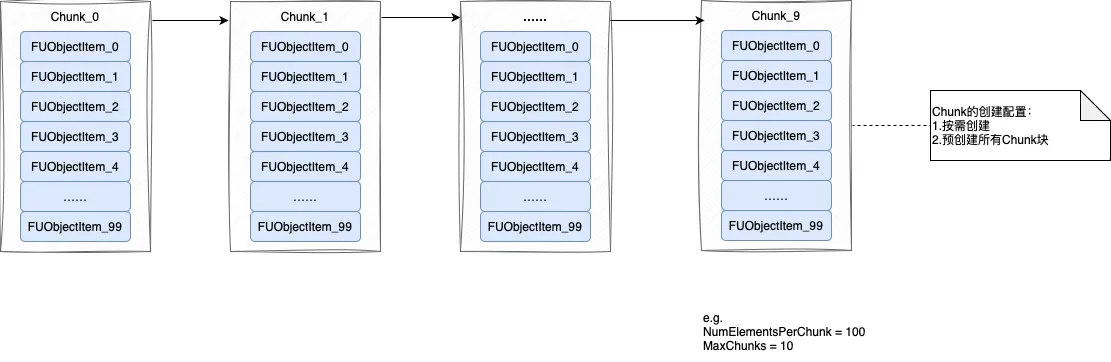
FUObjectArray的作用:
全量管理UObject
为UObject分配internalIndex(即UniqueID),提供接口:通过internalIndex获取到UObject对象
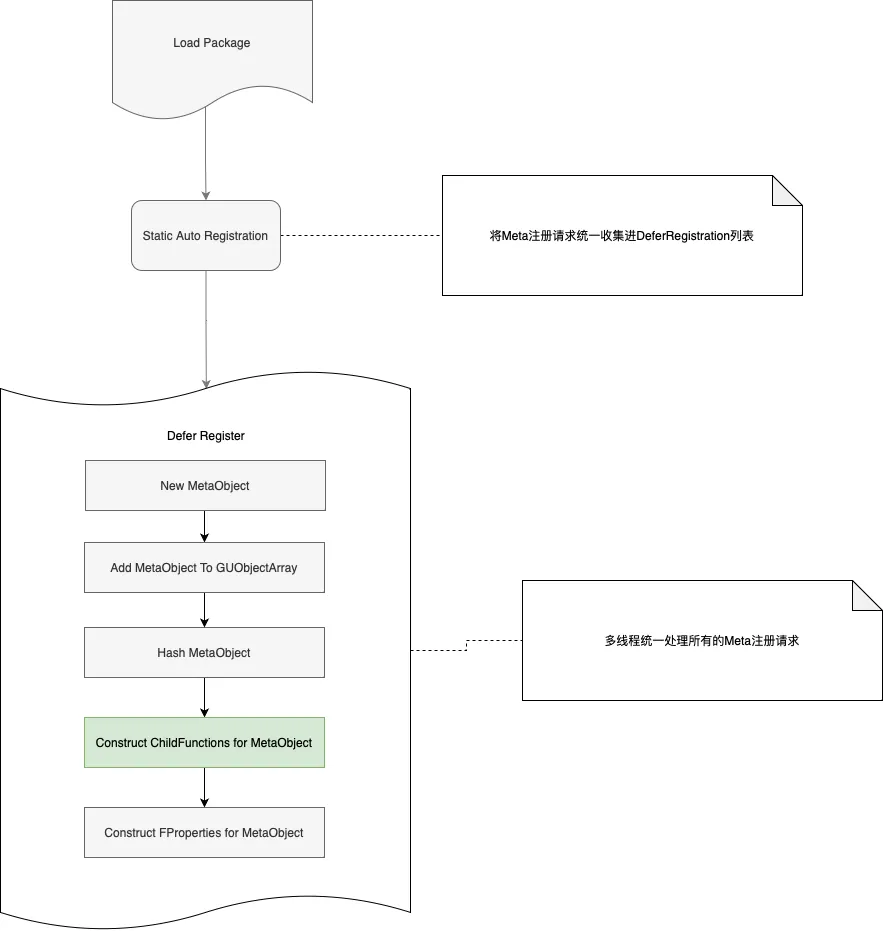
3.2.2.2.注册机制
static自动注册机制:UE自动生成的gen.cpp中,通过声明FRegisterCompiledInInfo类型的static变量,实现Meta自动注册。
// 声明FRegisterCompiledInInfo类型的static变量
static FRegisterCompiledInInfo Z_CompiledInDeferFile_FID_FortuneGame_Source_FortuneGame_AI_FGReflectionStructTest_h_1075197975(
TEXT("/Script/FortuneGame"),
nullptr,
0,
Z_CompiledInDeferFile_FID_FortuneGame_Source_FortuneGame_AI_FGReflectionStructTest_h_Statics::ScriptStructInfo,
UE_ARRAY_COUNT(Z_CompiledInDeferFile_FID_FortuneGame_Source_FortuneGame_AI_FGReflectionStructTest_h_Statics::ScriptStructInfo),
nullptr,
0);
struct FRegisterCompiledInInfo
{
template <typename ... Args>
FRegisterCompiledInInfo(Args&& ... args)
{
// 对象构造时执行注册逻辑
RegisterCompiledInInfo(std::forward<Args>(args)...);
}
};
延迟注册机制:上面代码中RegisterCompiledInInfo只是定义了一个注册任务,真实的Meta数据注册逻辑其实发生在之后的时间片内。(不属于反射重点关注内容,不进行代码展开)
引入延迟注册的目的:多线程加快处理速度。
总结而言,UScriptStruct的生成与注册流程总结如下:
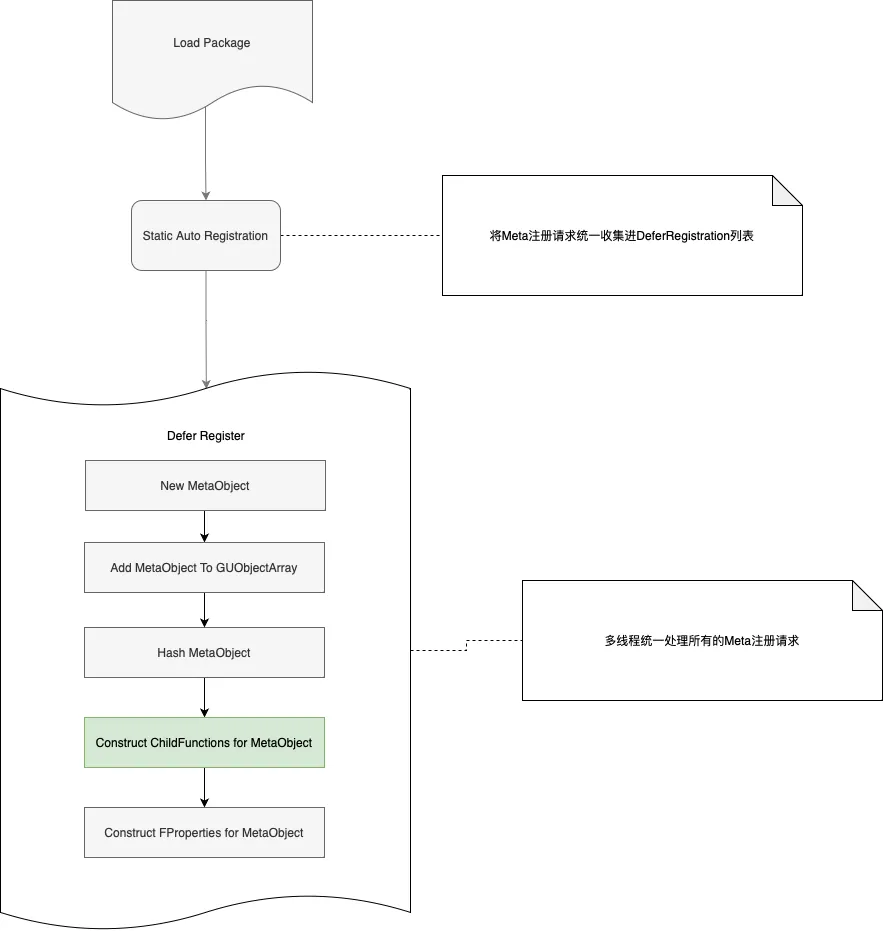
3.2.3.反射应用示例
FFGReflectionStructTest StructInstance;
// 根据名字查找Meta数据
UScriptStruct* StructObject = FindObject<UScriptStruct>(ANY_PACKAGE, UTF8_TO_TCHAR("FGReflectionStructTest")); // 注意:此处StructName需要去除F前缀
if (StructObject)
{
// 根据Meta数据实例化对象
StructObject->InitializeDefaultValue(reinterpret_cast<uint8*>(&StructInstance));
// 获取Field信息
TArray<FProperty*> Fields;
for (TFieldIterator<FProperty> It(StructObject); It; ++It)
{
FProperty* Property = *It;
FString FieldName = Property->GetName();
FString FieldType = Property->GetCPPType();
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Warning, TEXT("Field Name: %s, Field Type: %s"), *FieldName, *FieldType);
}
// 根据Field名字 Get/Set Field数据
FIntProperty *FieldProp = CastField<FIntProperty>(StructObject->FindPropertyByName(TEXT("TestVal")));
if(FieldProp)
{
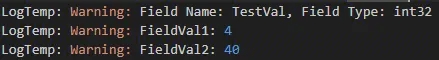
void* FieldAddr = FieldProp->ContainerPtrToValuePtr<void>(&StructInstance);
int32 FieldVal = FieldProp->GetPropertyValue(FieldAddr);
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Warning, TEXT("FieldVal1: %d"), FieldVal);
FieldProp->SetPropertyValue(FieldAddr, 40);
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Warning, TEXT("FieldVal2: %d"), StructInstance.TestVal);
}
}
输出:
3.3.Class反射实现
3.3.1.初探UClass
先创建一个最简单的class示例:
UCLASS()
class FORTUNEGAME_API UFGReflectionTest: public UObject
{
GENERATED_BODY()
public:
UPROPERTY()
int32 TestVal;
};
展开GENERATED_BODY
UCLASS()
class FORTUNEGAME_API UFGReflectionTest: public UObject
{
……
public:
// 稍后展开
DECLARE_CLASS(UFGReflectionTest, UObject, COMPILED_IN_FLAGS(0), CASTCLASS_None, TEXT("/Script/FortuneGame"), NO_API)
// 序列化相关
friend FArchive &operator<<( FArchive& Ar, UFGReflectionTest*& Res )
{
return Ar << (UObject*&)Res;
}
friend void operator<<(FStructuredArchive::FSlot InSlot, UFGReflectionTest*& Res)
{
InSlot << (UObject*&)Res;
}
// 构造与析构相关,不需要过多关注
/** Standard constructor, called after all reflected properties have been initialized */ \
NO_API UFGReflectionTest(const FObjectInitializer& ObjectInitializer = FObjectInitializer::Get()); \
private: \
/** Private move- and copy-constructors, should never be used */ \
NO_API UFGReflectionTest(UFGReflectionTest&&); \
NO_API UFGReflectionTest(const UFGReflectionTest&); \
public: \
DECLARE_VTABLE_PTR_HELPER_CTOR(NO_API, UFGReflectionTest); \
DEFINE_VTABLE_PTR_HELPER_CTOR_CALLER(UFGReflectionTest); \
DEFINE_DEFAULT_OBJECT_INITIALIZER_CONSTRUCTOR_CALL(UFGReflectionTest) \
NO_API virtual ~UFGReflectionTest();
public:
UPROPERTY()
int32 TestVal;
};
展开DECLARE_CLASS
UCLASS()
class FORTUNEGAME_API UFGReflectionTest: public UObject
{
……
public:
// DECLARE_CLASS(UFGReflectionTest, UObject, COMPILED_IN_FLAGS(0), CASTCLASS_None, TEXT("/Script/FortuneGame"), NO_API)
private:
UFGReflectionTest& operator=(UFGReflectionTest&&); // 禁用赋值操作
UFGReflectionTest& operator=(const UFGReflectionTest&); // 禁用赋值操作
NO_API static UClass* GetPrivateStaticClass(); // 获取Meta数据
public:
/** Typedef for the base class ({{ typedef-type }}) */
typedef UObject Super;
/** Typedef for {{ typedef-type }}. */
typedef UFGReflectionTest ThisClass;
/** Returns a UClass object representing this class at runtime */
inline static UClass* StaticClass()
{
return GetPrivateStaticClass();
}
/** Returns the package this class belongs in */
inline static const TCHAR* StaticPackage()
{
return TEXT("/Script/FortuneGame");
}
/** For internal use only; use StaticConstructObject() to create new objects. */
inline void* operator new(const size_t InSize, EInternal InInternalOnly, UObject* InOuter = (UObject*)GetTransientPackage(), FName InName = NAME_None, EObjectFlags InSetFlags = RF_NoFlags)
{
return StaticAllocateObject(StaticClass(), InOuter, InName, InSetFlags);
}
/** For internal use only; use StaticConstructObject() to create new objects. */
inline void* operator new( const size_t InSize, EInternal* InMem )
{
return (void*)InMem;
}
/* Eliminate V1062 warning from PVS-Studio while keeping MSVC and Clang happy. */
inline void operator delete(void* InMem)
{
::operator delete(InMem);
}
……
public:
UPROPERTY()
int32 TestVal;
};
可以看出,UE为class定义的Meta数据类型为UClass。
虽然相比struct,class定义中多出很多接口,但在解析UClass反射实现时,这些新增内容可以暂时忽略。
相比struct,class最重要的不同点其实在于:成员函数注册。
3.3.1.1.FClassParam
与UStruct类似,UE为构造UClass数据,定义了一套构造参数:FClassParams
// UClass需要维护依赖关系
UObject* (*const Z_Construct_UClass_UFGReflectionTest_Statics::DependentSingletons[])() = {
(UObject* (*)())Z_Construct_UClass_UObject,
(UObject* (*)())Z_Construct_UPackage__Script_FortuneGame,
};
// StaticClass()调用GetPrivateStaticClass(),如果Meta UClass未被创建,则不自动创建
// 相比FStructParams,多了依赖关系,多了functionArray,多了ImplementedInterfaceArray
struct FClassParams
{
UClass* (*ClassNoRegisterFunc)(); // UClass的部分内容构建接口
const char* ClassConfigNameUTF8; // name
const FCppClassTypeInfoStatic* CppClassInfo; // 是否为virtual class
UObject* (*const *DependencySingletonFuncArray)(); // 依赖关系
const FClassFunctionLinkInfo* FunctionLinkArray; // 函数列表
const FPropertyParamsBase* const* PropertyArray; // 成员列表
const FImplementedInterfaceParams* ImplementedInterfaceArray; // 已实现的接口列表
int32 NumDependencySingletons;
int32 NumFunctions;
int32 NumProperties;
int32 NumImplementedInterfaces;
uint32 ClassFlags; // EClassFlags
#if WITH_METADATA
const FMetaDataPairParam* MetaDataArray;
int32 NumMetaData;
#endif
};
相比FStructParams,FClassParams增加了依赖关系,FunctionLinkArray,ImplementedInterfaceArray。
3.3.1.2.Meta注册流程
相比于struct,class进行Meta数据注册时,最明显的变化是新增了ChildFunctions的构造。
3.3.2.构造ChildFunctions
为我们的class示例新增一个简单的UFUNCTION:
UCLASS()
class FORTUNEGAME_API UFGReflectionTest: public UObject
{
GENERATED_BODY()
public:
UPROPERTY()
int32 TestVal;
UFUNCTION()
int32 TestFunc(int InParam1, int InParam2) {return InParam1 + InParam2;}
};
3.3.2.1.构造static exec函数
UE生成的代码有了如下部分新增:
#define FID_FortuneGame_Source_FortuneGame_AI_FGReflectionTest_h_11_RPC_WRAPPERS \
\
DECLARE_FUNCTION(execTestFunc);
// 展开DECLARE_FUNCTION
static void execTestFunc( UObject* Context, FFrame& Stack, RESULT_DECL )
// 对execTestFunc的实现
void execTestFunc( UObject* Context, FFrame& Stack, RESULT_DECL )
{
P_GET_PROPERTY(FIntProperty,Z_Param_InParam1);
P_GET_PROPERTY(FIntProperty,Z_Param_InParam2);
P_FINISH;
P_NATIVE_BEGIN;
*(int32*)Z_Param__Result=P_THIS->TestFunc(Z_Param_InParam1,Z_Param_InParam2);
P_NATIVE_END;
}
// 展开宏
void execTestFunc( UObject* Context, FFrame& Stack, void*const Z_Param__Result)
{
int32 Z_Param_InParam1= FIntProperty::GetDefaultPropertyValue();
Stack.StepCompiledIn<FIntProperty>(&Z_Param_InParam1);
int32 Z_Param_InParam2= FIntProperty::GetDefaultPropertyValue();
Stack.StepCompiledIn<FIntProperty>(&Z_Param_InParam2);
*(int32*)Z_Param__Result=P_THIS->TestFunc(Z_Param_InParam1,Z_Param_InParam2);
}
很明显,上述代码为TestFunc构造了一个全局static函数,准备传递给function的Meta对象。
3.3.2.2.构造function的Meta对象
UE为function定义的Meta数据类型为UFunction
与class/struct类似,UE为构造UFunction数据,定义了一套构造参数:FFunctionParams
struct FFunctionParams
{
UObject* (*OuterFunc)(); // 所属class的UClass对象
UFunction* (*SuperFunc)(); // 继承函数的Meta对象
const char* NameUTF8; // 函数名
const char* OwningClassName; // 委托相关,暂不关注
const char* DelegateName; // 委托相关,暂不关注
SIZE_T StructureSize; // 函数参数结构的size
const FPropertyParamsBase* const* PropertyArray; // 函数参数列表
int32 NumProperties; // 函数参数个数
EObjectFlags ObjectFlags;
EFunctionFlags FunctionFlags;
uint16 RPCId;
uint16 RPCResponseId;
#if WITH_METADATA
const FMetaDataPairParam* MetaDataArray;
int32 NumMetaData;
#endif
};
UE为上述示例UFGReflectionTest生成的FFunctionParams数据如下:
struct Z_Construct_UFunction_UFGReflectionTest_TestFunc_Statics
{
// 参数数据结构,return值也在该结构中 该结构定义在此的最重要作用,是计算出函数参数所需size
struct FGReflectionTest_eventTestFunc_Parms
{
int32 InParam1;
int32 InParam2;
int32 ReturnValue;
};
static const UECodeGen_Private::FUnsizedIntPropertyParams NewProp_InParam1;
static const UECodeGen_Private::FUnsizedIntPropertyParams NewProp_InParam2;
static const UECodeGen_Private::FIntPropertyParams NewProp_ReturnValue;
static const UECodeGen_Private::FPropertyParamsBase* const PropPointers[];
#if WITH_METADATA
static const UECodeGen_Private::FMetaDataPairParam Function_MetaDataParams[];
#endif
static const UECodeGen_Private::FFunctionParams FuncParams;
};
// 为每一个参数定义的主要内容包括:名字、引用标志、参数在FGReflectionTest_eventTestFunc_Parms结构中的偏移
const UECodeGen_Private::FUnsizedIntPropertyParams Z_Construct_UFunction_UFGReflectionTest_TestFunc_Statics::NewProp_InParam1 = {
"InParam1",
nullptr,
(EPropertyFlags)0x0010000000000080,
UECodeGen_Private::EPropertyGenFlags::Int, RF_Public|RF_Transient|RF_MarkAsNative,
1,
nullptr,
nullptr,
STRUCT_OFFSET(FGReflectionTest_eventTestFunc_Parms, InParam1),
METADATA_PARAMS(nullptr, 0)
};
const UECodeGen_Private::FUnsizedIntPropertyParams Z_Construct_UFunction_UFGReflectionTest_TestFunc_Statics::NewProp_InParam2 = {
"InParam2",
nullptr,
(EPropertyFlags)0x0010000000000080,
UECodeGen_Private::EPropertyGenFlags::Int, RF_Public|RF_Transient|RF_MarkAsNative,
1,
nullptr,
nullptr,
STRUCT_OFFSET(FGReflectionTest_eventTestFunc_Parms, InParam2),
METADATA_PARAMS(nullptr, 0)
};
const UECodeGen_Private::FIntPropertyParams Z_Construct_UFunction_UFGReflectionTest_TestFunc_Statics::NewProp_ReturnValue = {
"ReturnValue",
nullptr,
(EPropertyFlags)0x0010000000000580,
UECodeGen_Private::EPropertyGenFlags::Int,
RF_Public|RF_Transient|RF_MarkAsNative,
1,
nullptr,
nullptr,
STRUCT_OFFSET(FGReflectionTest_eventTestFunc_Parms, ReturnValue),
METADATA_PARAMS(nullptr, 0)
};
// UFunction会将参数作为属性,将参数维护进入childProperty列表
const UECodeGen_Private::FPropertyParamsBase* const Z_Construct_UFunction_UFGReflectionTest_TestFunc_Statics::PropPointers[] = {
(const UECodeGen_Private::FPropertyParamsBase*)&Z_Construct_UFunction_UFGReflectionTest_TestFunc_Statics::NewProp_InParam1,
(const UECodeGen_Private::FPropertyParamsBase*)&Z_Construct_UFunction_UFGReflectionTest_TestFunc_Statics::NewProp_InParam2,
(const UECodeGen_Private::FPropertyParamsBase*)&Z_Construct_UFunction_UFGReflectionTest_TestFunc_Statics::NewProp_ReturnValue,
};
#if WITH_METADATA
const UECodeGen_Private::FMetaDataPairParam Z_Construct_UFunction_UFGReflectionTest_TestFunc_Statics::Function_MetaDataParams[] = {
{ "ModuleRelativePath", "AI/FGReflectionTest.h" },
};
#endif
const UECodeGen_Private::FFunctionParams Z_Construct_UFunction_UFGReflectionTest_TestFunc_Statics::FuncParams = {
(UObject*(*)())Z_Construct_UClass_UFGReflectionTest,
nullptr,
"TestFunc",
nullptr,
nullptr,
sizeof(Z_Construct_UFunction_UFGReflectionTest_TestFunc_Statics::FGReflectionTest_eventTestFunc_Parms),
Z_Construct_UFunction_UFGReflectionTest_TestFunc_Statics::PropPointers,
UE_ARRAY_COUNT(Z_Construct_UFunction_UFGReflectionTest_TestFunc_Statics::PropPointers),
RF_Public|RF_Transient|RF_MarkAsNative, (EFunctionFlags)0x00020401,
0,
0,
METADATA_PARAMS(Z_Construct_UFunction_UFGReflectionTest_TestFunc_Statics::Function_MetaDataParams,
UE_ARRAY_COUNT(Z_Construct_UFunction_UFGReflectionTest_TestFunc_Statics::Function_MetaDataParams))
};
FFunctionParams中的内容,会分散赋值到UFunction与FProperty对象中:
UFunction结构的重要字段解析:
NumParms记录参数个数,包含returnValue
ParmsSize维护参数结构所需的内存size
ReturnValueOffset维护returnValue在参数结构中的偏移
Func维护对应static exec函数的指针
ChildProperties维护第一个参数的FProperty对象指针
FProperty结构的重要字段解析:
ElementSize记录field的内存size
Offset_Internal记录field在所属类型中的地址偏移
Owner记录field的所属类型Meta数据
Next为所属类型维护下一个参数的FProperty数据指针
NamePrivate记录参数名字
根据UFunction对象中的ChildProperties数据 与 FProperty中的Next数据,便能够拿到function中所有参数的FProperty数据。
3.3.3.维护UClass与UFunction的关联关系
重新看回UE为class生成的FClassParams 数据:
// class中的UFunction构造列表
const FClassFunctionLinkInfo Z_Construct_UClass_UFGReflectionTest_Statics::FuncInfo[] = {
{ &Z_Construct_UFunction_UFGReflectionTest_TestFunc, "TestFunc" }, // 1382218509
};
const UECodeGen_Private::FClassParams Z_Construct_UClass_UFGReflectionTest_Statics::ClassParams = {
&UFGReflectionTest::StaticClass,
nullptr,
&StaticCppClassTypeInfo,
DependentSingletons,
FuncInfo, // 上面的UFunction构造列表
Z_Construct_UClass_UFGReflectionTest_Statics::PropPointers,
nullptr,
UE_ARRAY_COUNT(DependentSingletons),
UE_ARRAY_COUNT(FuncInfo), // 上面的UFunction构造列表个数
UE_ARRAY_COUNT(Z_Construct_UClass_UFGReflectionTest_Statics::PropPointers),
0,
0x001000A0u,
METADATA_PARAMS(Z_Construct_UClass_UFGReflectionTest_Statics::Class_MetaDataParams, UE_ARRAY_COUNT(Z_Construct_UClass_UFGReflectionTest_Statics::Class_MetaDataParams))
};
ClassParams 中的FunctionLinkArray被赋值为FuncInfo[] ,然后将生成的UFunction对象绑定到UClass对象上:
void UClass::CreateLinkAndAddChildFunctionsToMap(const FClassFunctionLinkInfo* Functions, uint32 NumFunctions)
{
for (; NumFunctions; --NumFunctions, ++Functions)
{
const char* FuncNameUTF8 = Functions->FuncNameUTF8;
UFunction* Func = Functions->CreateFuncPtr();
Func->Next = Children;
Children = Func;
AddFunctionToFunctionMap(Func, FName(UTF8_TO_TCHAR(FuncNameUTF8)));
}
}
FClassParams中的内容,会分散赋值到UClass、UFunction与FProperty对象中:
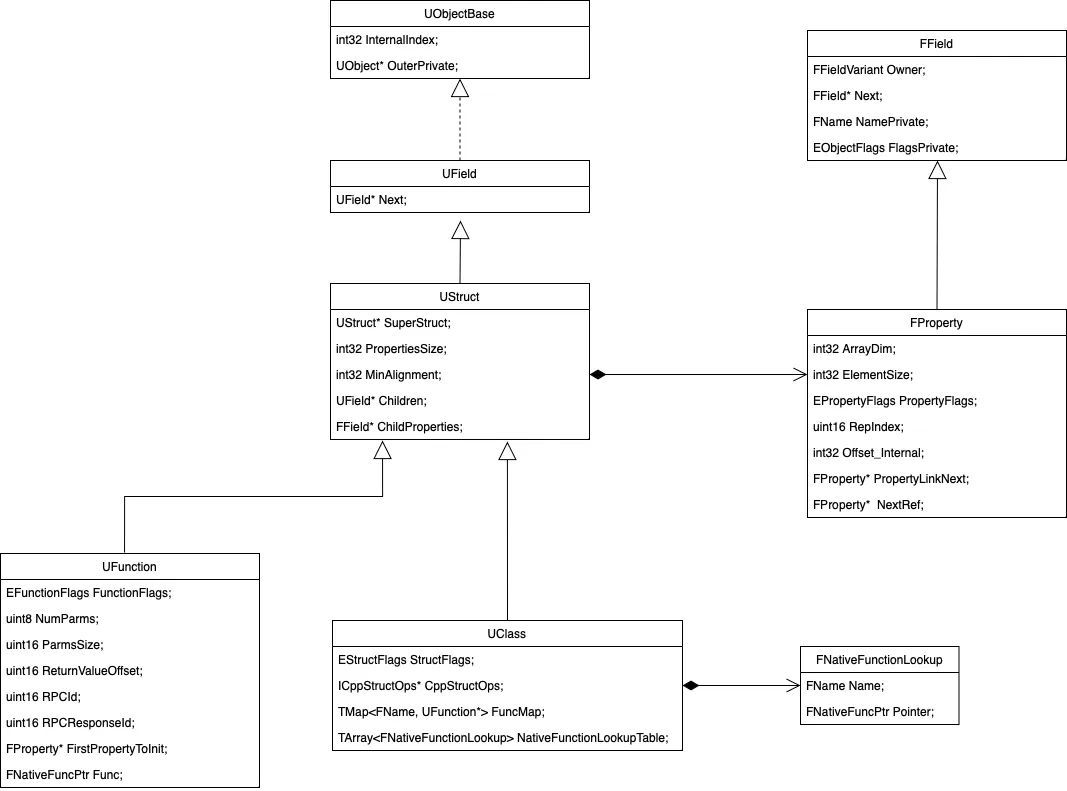
UClass结构的重要字段解析:
FuncMap为class中的所有函数建立name到UFunction*的映射关系
NativeFunctionLookupTable为class中的所有原生函数维护static函数指针列表
ChildProperties维护class中首个field的FProperty数据指针
UField* Children维护首个函数的UFunction数据指针
SuperStruct维护父结构的Meta对象指针
UFunction结构的额外字段解析:
- Next为所属类型维护下一个函数的UFunction数据指针
根据UClass对象中的Children数据 与 UFunction中的Next数据,便能够拿到class中所有函数的UFunction数据。
3.3.4.反射应用示例
// 通过函数名字调用函数执行
UObject* Object = NewObject<UObject>(GetTransientPackage(), TEXT("UFGReflectionTest")); // 创建一个类实例
UClass* MyClass = FindObject<UClass>(ANY_PACKAGE, UTF8_TO_TCHAR("FGReflectionTest"));
for (TFieldIterator<UFunction> FunctionIterator(MyClass); FunctionIterator; ++FunctionIterator)
{
UFunction* Function = *FunctionIterator;
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Warning, TEXT("Function Name: %s"), *Function->GetName());
}
FName FunctionName = TEXT("TestFunc"); // 要调用的函数名字
UFunction* Function = MyClass->FindFunctionByName(FunctionName);
if (Function)
{
uint8* AllFunctionParam = static_cast<uint8*>(FMemory_Alloca(Function->ParmsSize));
FMemory::Memzero(AllFunctionParam, Function->ParmsSize);
FFrame Frame(nullptr, Function, AllFunctionParam);
// 设置函数的参数值
for (TFieldIterator<FProperty> It(Function); It; ++It)
{
FProperty* Param = *It;
if (Param->HasAnyPropertyFlags(CPF_Parm))
{
// 根据参数类型设置参数值
if (Param->GetName() == "InParam1")
{
FIntProperty* IntParam = CastField<FIntProperty>(Param);
int32 ParamValue = 42; // 设置整数参数值
IntParam->SetPropertyValue_InContainer(Frame.Locals, ParamValue);
}
else if (Param->GetName() == "InParam2")
{
FIntProperty* IntParam = CastField<FIntProperty>(Param);
int32 ParamValue = 58; // 设置整数参数值
IntParam->SetPropertyValue_InContainer(Frame.Locals, ParamValue);
}
}
}
Object->ProcessEvent(Function, AllFunctionParam);
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Warning, TEXT("函数返回值为:%d"), *(AllFunctionParam + Function->ReturnValueOffset));
}
输出结果:
UObject会注册ExecuteUbergraph函数,因此输出函数中会比预想的多出一个。
// UObject会默认注册ExecuteUbergraph函数
const FClassFunctionLinkInfo Z_Construct_UClass_UObject_Statics::FuncInfo[] = {
{ &Z_Construct_UFunction_UObject_ExecuteUbergraph, "ExecuteUbergraph" }, // 3729755051
};
3.3.5.引用传参的处理
为我们的class示例新增一个简单的UFUNCTION,里面使用引用传参:
UFUNCTION()
int32 TestFuncPlus(int32 &InParam1, int32 &InParam2) {
InParam1 = InParam2;
return InParam1;
}
UE自动生成的exec函数中,获取参数时换为了P_GET_PROPERTY_REF:
#define P_GET_PROPERTY_REF(PropertyType, ParamName) \
PropertyType::TCppType ParamName##Temp = PropertyType::GetDefaultPropertyValue(); \
PropertyType::TCppType& ParamName = Stack.StepCompiledInRef<PropertyType, PropertyType::TCppType>(&ParamName##Temp);
DEFINE_FUNCTION(UFGReflectionTest::execTestFuncPlus)
{
P_GET_PROPERTY_REF(FIntProperty,Z_Param_Out_InParam1);
P_GET_PROPERTY_REF(FIntProperty,Z_Param_Out_InParam2);
*(int32*)Z_Param__Result=P_THIS->TestFuncPlus(Z_Param_Out_InParam1,Z_Param_Out_InParam2);
}
代码中Stack.StepCompiledInRef会返回传入参数的数据引用,以此实现反射时对引用传参函数的调用。
3.4.Enum反射实现
先创建一个最简单的enum示例:
UENUM()
enum class EFGReflectionEnumTest : uint8
{
Type1,
Type2,
};
生成的代码gen.h
// 循环处理宏
#define FOREACH_ENUM_EFGREFLECTIONENUMTEST(op) \
op(EFGReflectionEnumTest::Type1) \
op(EFGReflectionEnumTest::Type2)
enum class EFGReflectionEnumTest : uint8;
template<> struct TIsUEnumClass<EFGReflectionEnumTest> { enum { Value = true }; };
template<> FORTUNEGAME_API UEnum* StaticEnum<EFGReflectionEnumTest>();
可以看出,UE为enum定义的Meta数据类型为UEnum。
理所当然,UE为构造UEnum数据,定义了一套构造参数:FEnumParams
struct FEnumParams
{
UObject* (*OuterFunc)(); // 获取enum定义所在的UObject
FText (*DisplayNameFunc)(int32); // 自定义的enum别名输出函数
const char* NameUTF8; // enum名字
const char* CppTypeUTF8; // 数据类型名
const FEnumeratorParam* EnumeratorParams; // 枚举值的定义
int32 NumEnumerators; // 枚举值个数
EObjectFlags ObjectFlags;
EEnumFlags EnumFlags;
uint8 CppForm; // this is of type UEnum::ECppForm
#if WITH_METADATA
const FMetaDataPairParam* MetaDataArray;
int32 NumMetaData;
#endif
};
UE在自动生成的gen.cpp结构中,为EFGReflectionEnumTest 实例化的FEnumParams对象如下:
const UECodeGen_Private::FEnumeratorParam Z_Construct_UEnum_FortuneGame_EFGReflectionEnumTest_Statics::Enumerators[] = {
{ "EFGReflectionEnumTest::Type1", (int64)EFGReflectionEnumTest::Type1 },
{ "EFGReflectionEnumTest::Type2", (int64)EFGReflectionEnumTest::Type2 },
};
const UECodeGen_Private::FEnumParams Z_Construct_UEnum_FortuneGame_EFGReflectionEnumTest_Statics::EnumParams = {
(UObject*(*)())Z_Construct_UPackage__Script_FortuneGame,
nullptr,
"EFGReflectionEnumTest",
"EFGReflectionEnumTest",
Z_Construct_UEnum_FortuneGame_EFGReflectionEnumTest_Statics::Enumerators,
UE_ARRAY_COUNT(Z_Construct_UEnum_FortuneGame_EFGReflectionEnumTest_Statics::Enumerators),
RF_Public|RF_Transient|RF_MarkAsNative,
EEnumFlags::None,
(uint8)UEnum::ECppForm::EnumClass,
METADATA_PARAMS(Z_Construct_UEnum_FortuneGame_EFGReflectionEnumTest_Statics::Enum_MetaDataParams, UE_ARRAY_COUNT(Z_Construct_UEnum_FortuneGame_EFGReflectionEnumTest_Statics::Enum_MetaDataParams))
};
FEnumParams所包含的内容,会被赋值到各个不同的结构中:
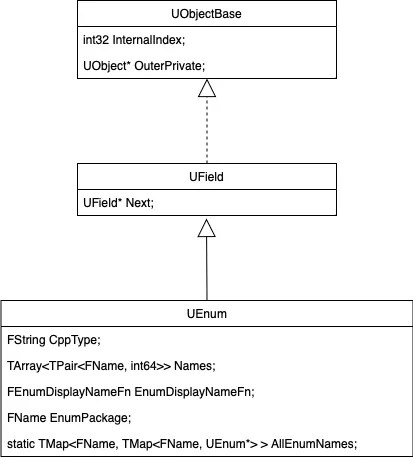
UEnum结构的重要字段解析:
Names维护enum名字与value的映射对
EnumDisplayNameFn维护用户自定义的enum别名输出函数
EnumPackage记录enum定义所在package的名字
AllEnumNames维护全局数据:package内的所有UEnum数据
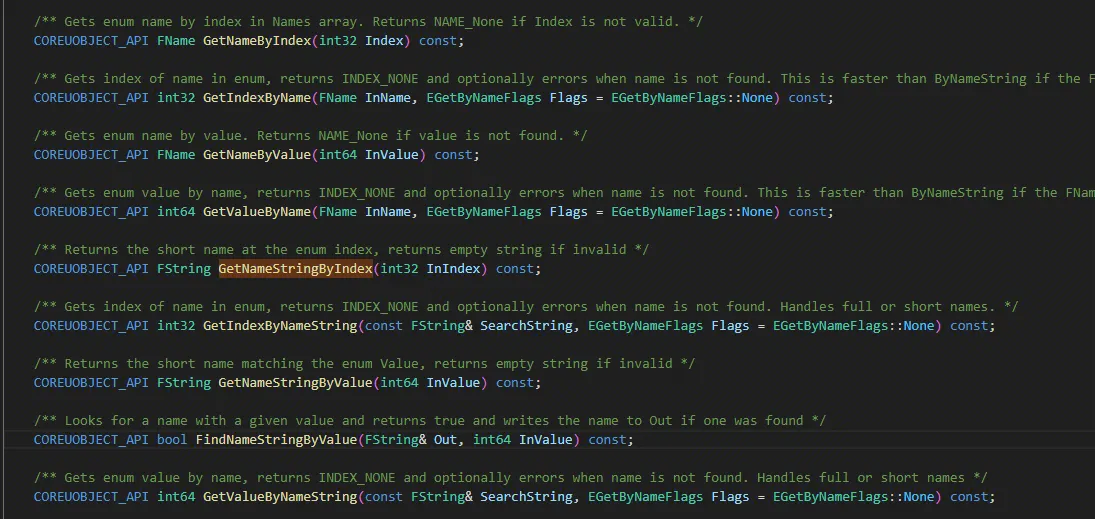
另外UEnum提供了大量反射相关接口:
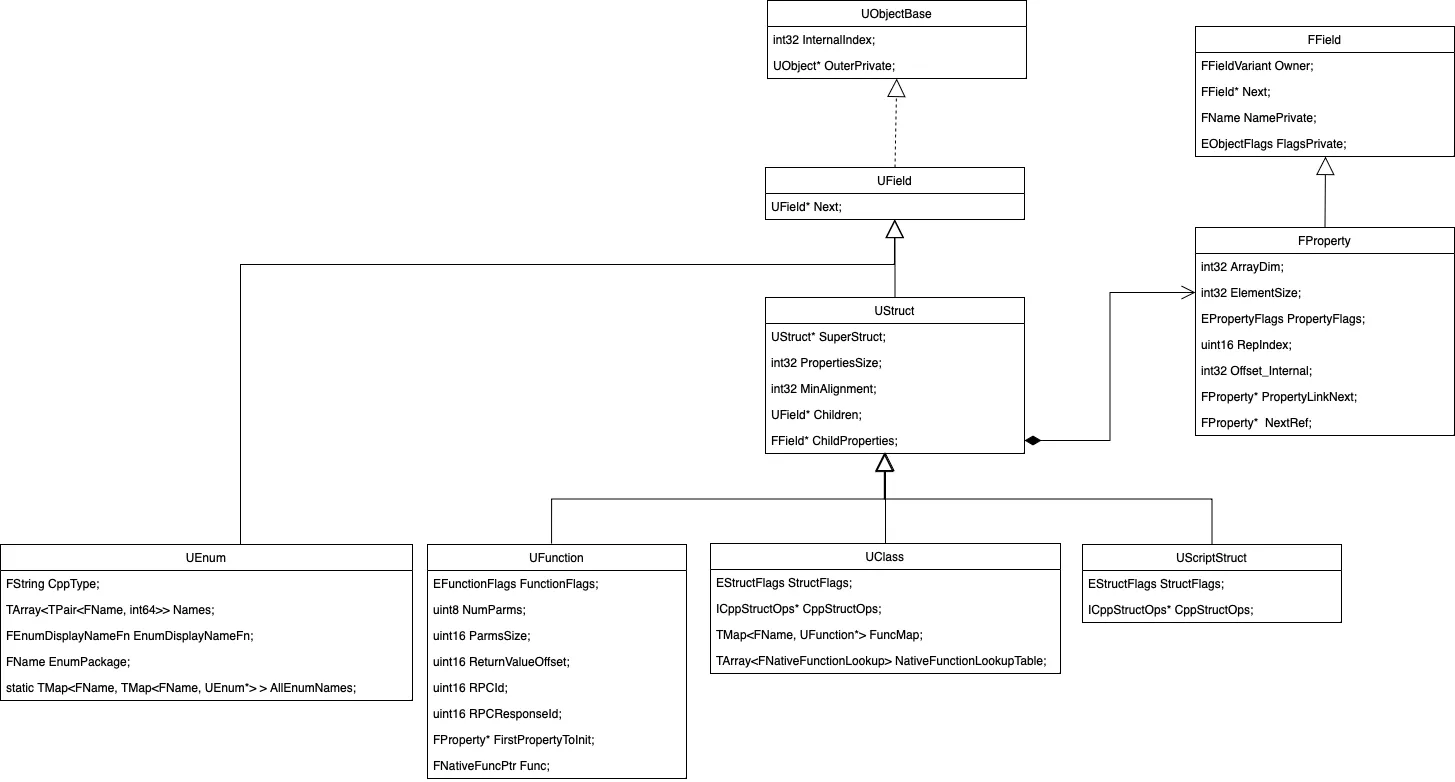
3.5.UE反射系统实现概览
根据上述Struct、Class、Enum的反射实现,总结出UE反射系统实现概览图如下:
3.6.总结
相比于piccolo,UE的反射系统实现复杂得多,不论是结构关系还是功能层次都显得更加晦涩。
但不可否认的是UE为这套反射系统实现了无比完善的功能特性,也为运行性能做了一定的优化实现。
最后,希望这篇文章能对大家理解与使用UE反射系统有所帮助。