SFU模式PeerConnection建立过程与Ice-Lite理解
原文出处:WebRTC中PeerConnection建立连接过程介绍
WebRTC 中数据传输都是通过被称为 PeerConnection 的对象来完成的,PeerConnection 在可以传输数据前的建立过程现对于传统的C/S 模式有略微差别,类似于 P2P 连接的建立过程,并且复用了传统的 STUN/TURN/ICE 架构的 P2P 实现方式。由于 WebRTC 支持MESH/SFU/MCU 三种模式,使用 PeerConnection 概念的好处是可以同时兼容这三种模式,即使是像 SFU/MCU 这种非 P2P 的场景也同样使用 PeerConnection 来建立传输通道,不过针对 SFU/MCU 场景已经有一些优化方案,例如 ice-lite 。本文介绍了 P2P 和 SFU 场景中 PeerConnection 建立的过程。
WebRTC PeerConnection 建立过程
常规的 WebRTC PeerConnection 通信过程中有四种角色:
Signaling Server
STUN/TURN/ICE Server
Local Peer
Remote Peer
通信过程中的基本概念:
Room: Signaling Server 使用 Room 的概念对一组通信的 peers 进行管理,一个 Room 中包含 一个或多个 peers,当没有 peers 存在时 Room 自动注销;当第一个 peer 连接到 Signaling Server 时执行 Create Room 操作;
Offer/Answer:描述 peer 媒体属性的 SDP 信息通过 Offer/Answer 模式,由 Signaling Server 进行交换,通信建立前两个互相通信的 peer 需要互相获得对方的 媒体 SDP 信息;
IceCandidate: Peer 与 STUN/TURN/ICE Server 通信,获取自己的 NAT 类型以及公网IP和端口,这些消息简称为 IceCandidate。和 媒体描述信息一样,IceCandidate 信息也需要互相通信的 peer 在通信前进行交换,在获取到对方的 iceCandidate 信息后双方通过 Stun binding 信令确认信道的联通性;
下图为经典的 WebRTC 中 PeerConnection 连接建立流程图:
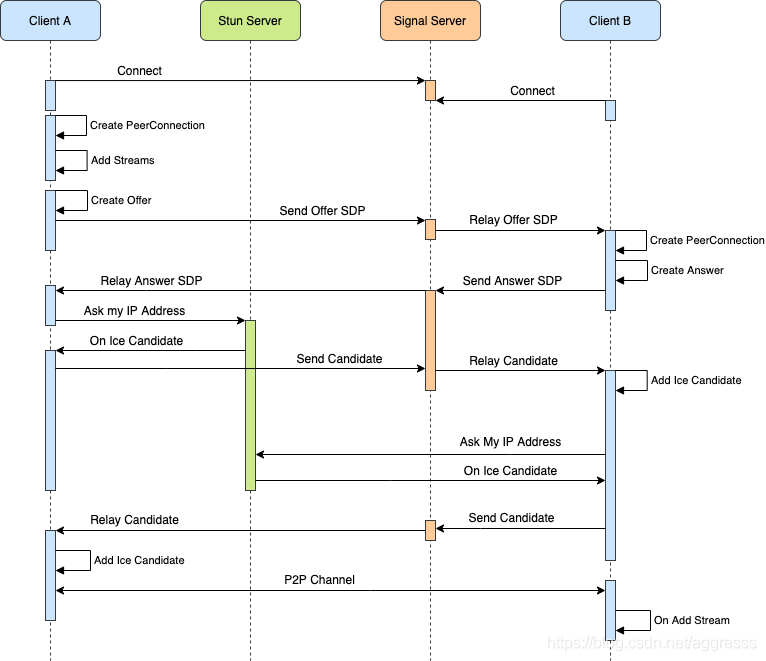
通过上面的流程图可以总结出一下几点:
1、peerConnnection 建立之前必须交换两个信息:SDP 和 iceCandidate;
2、Answer 端接收到 Offer 后才会创建 PeerConnection 对象;
3、Offer 端在创建成功本地 Offer 后才会去收集本地 iceCandidate;Answer 端在创建成功本地 Answer 后才会去收集本地iceCandidate;
4、peerConnection 两端都收到 iceCandidate 后才完成 peerConnection 的建立。
使用 Web API 建立简单 peerConnection 的大概流程为:
1、创建 peerConnection 对象 pc = new RTCPeerConnection(null);当初始化参数中 iceServers 为空时只能创建本地连接;
2、设置peerConnection 对象 事件响应操作pc.addEventListener(‘icecandidate’, xxx) // icecandidate 通知,WebRTC 默认开启了trickle-ice,所以每探测到一个 iceCandidate 都会触发一次该事件,直到事件返回为 null 时,表示完成 iceCandidate探测;
3、pc.addEventListener(‘iceconnectionstatechange’, xxx) // ice 状态改变
4、pc.addEventListener(‘track’, xxx) // 接收到 track
5、执行 peerConnection 操作
6、pc.addTrack() 为 peerConnection 增加媒体流;
7、pc.createOffer() / pc.createAnswer() 创建 SDP Offer / SDP Answer
8、pc.setLocalDescription() Offer 端创建 Offer 后,Answer 端创建 Answer 后,将本地生成的 SDP 信息加入到本地 peerConnection;注意:iceCandidate 的收集过程发生在这个操作之后;
9、pc.setRemoteDescription() Answer 端接收到 Offer 后,Offer 端接收到 Answer 后,将对端的 SDP 信息加入到本地 peerConnection;
10、pc.addIceCandidate() 将对端生成的 iceCandidate 加入到本地 peerConneciton 的 ICE 代理中;
上面这个示例中使用到了 trickle-ice 协议,在 WebRTC 的 SDP 中通常可以包含三类信息
ICE Parameters: candidate/ice-ufrag/ice-pwd
DTLS Parameters: fingerprint/setup
Media Parameters: extmap/rtpmap/fmtp/rtcp-fb/ssrc
也就是说 iceCandidate 信息是可以放到 SDP 里面的,省去了一次信息交换的过程,但是 iceCandidate 的收集过程是比较耗时的,所以 WebRTC 里面启用了 trickle-ice,上面示例中 createOffer 产生的 SDP 里面并没有 iceCandidate 信息,而是在 peerConnection 执行 setLocalDescription 操作后才开始收集 iceCandidate,收集到一个便触发一次 icecandidate 事件,然后通过信令通道输出到对端 peerConnection,对端 peerConneciton 通过执行 addIceCandidate 操作将对端的 iceCandidate 添加到本地 peerConnection 的 ICE agent 中。
SFU 模式 PeerConnection 建立过程
SFU 模式下,SFU 服务都会有自己的固定公网IP地址,这个先决条件简化了 WebRTC 中 peerConnection 的建立过程,可以把这种场景理解为 P2P 通信的一端确定在 NAT 前面,并且有固定IP地址的特殊情况,这时对于 SFU 服务没有必要再去收集自己的 iceCandidate,所以 ICE 协议(RFC5245) 中定义了一种 lite 实现方式,简化了有固定IP公网地址一端的 ice 实现方式,只要满足固定公网IP的前提条件,通过 lite 方式实现一个 ice server,完全实现 ice 协议的对端将毫无感知的与 lite 实现建立常规的 peerConnection 通信信道。
ice-lite 有以下几个特点:
1、ICE 的 Lite 实现不需要实现 Candidate 的收集过程;只需要提供 Host Candidate;
2、不需要实现连通性检查或者状态机,只需要实现连通性检查的Response;
3、ICE Lite 在交互过程中只能是 controlled 角色,并且不能使用 USE-CANDIDATE 来做 ice nomination;
4、常规的 SFU 都会自身集成一个 ice lite 实现的 ice server,所以交互过程中省去了 ice server 的独立角色。SFU 的 SDP 信息中会携带自身的 Host Candidate 和 ‘a=ice-lite’ 属性,当对端收到 ‘a=ice-lite’ 属性后会自动将自己设置成 controlling 角色,主动与 SFU 的 ice agent 进行交互。同时 SFU 也不需要对端的 iceCandidate 信息,因为在对端发起 stun binding 测试连通性的时候就可以获取对端的信息,便可以建议一个 Transport tuple 用来维持 peerConnection 通信。
下图是 SFU 模式下 peerConnectionn 的建立过程:
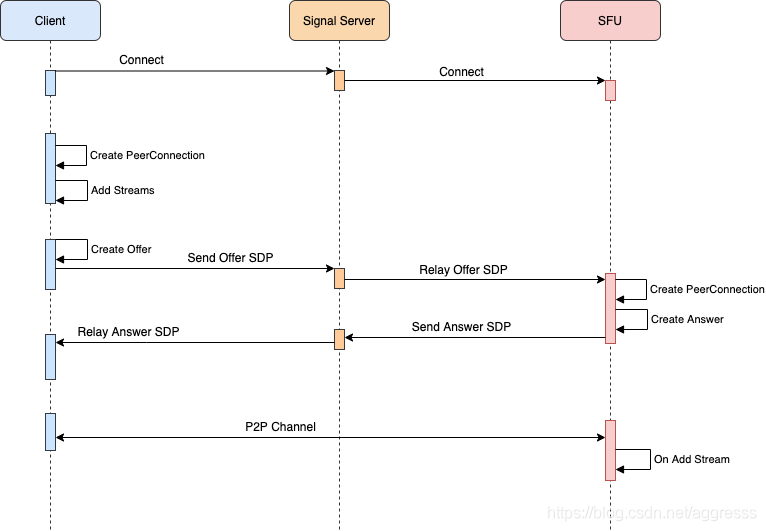
通过上面的流程图可以看出,在 SFU 场景下 peerConnection 的过程得到了简化,由于 SFU 具有固定公网 IP 地址和 ice-lite 实现的 ice server 加持,省去了 peerConnection 双方单独交换 iceCandidate 的流程,并且可以缩短 peerConnection 的建立时间。
原文出处:Ice-Lite 理解
It is not necessary to have a STUN server to get a webrtc peer connection between a full ICE implementation and an ICE lite implementation. This is because the ICE lite peer will use Peer Reflexive Candidates to get candidates for the full ICE peer behind a NAT. 在完整的ICE实现和ICE lite实现之间获得webrtc对等连接并不需要有STUN服务器。这是因为ICE lite 一方会根据Peer Reflexive Candidates去获得Full ICE peer一方的候选地址.
mattm, you only get reflexive candidate from a stun server. If your client is ICE-lite, then it generates only host candidates, if your client is full ice AND a stun server is provided, then that client is also generating srflx candidates and sending them to the other (possibly ice-lite) client. So the ice-lire client does not need to have access to a STUN server, but the full ice client needs. There is still a need for a STUN server in your solution. mattm,你只能通过stun server 来获得reflexive candidate. 如果你的是 ICE-lite的客户端, 只会生成host 的候选者. 如果你的客户端是full ice并且提供了一个Stun server, 这时候客户端是可以提供 srflx 的候选者, 并且发送他们给对方(可以是一个ice lite 客户端.). 因此,ice-lite客户端不需要访问STUN服务器,但是完整的ice客户端需要。在您的解决方案中仍然需要一个STUN服务器。
You only get server reflexive candidates from a STUN server. When an ICE lite peer receives traffic during the course of connection checks, it can respond to the source address as visible to it on the incoming packet (the peer reflexive candidate). I have setup connections between a full ICE and ICE lite implementations behind separate NATs successfully without using a STUN server. I believe these were all standard conforming. 您只能从STUN服务器获得服务器自反候选。当一个ICE-lite对等端在连接检查过程中接收到流量时,它可以在传入的数据包上对源地址做出响应(对等端自反候选者)。我在独立的nat之后成功地在一个完整的ICE和ICE-lite实现之间建立了连接,而不使用STUN服务器。我相信这些都符合标准。
In ICE lite procedure, client doesn't gathers all the candidates but only the local host candidate. This is basically designed for end point which is behind public IP address, when a client is behind a public IP where there is no NAT, it can connect with any other candidate even if that other end is behind Symmetric NAT. ICE-Lite doesn't require STUN/TURN server. You can not achieve this using the SDP line as ICE-Lite procedure comes first before you get the candidates. So if you don't set STUN/TURN server then it will work as ICE-Lite (though its not formal way of having ICE-lite, ICE client should have the defined way to set ICE-Full or ICE-Lite) as now it will just gather the host candidates. But if your end point is behind some NAT and other end point is out of the network then it will not work. So better if you could determine if the client is behind public IP or not.
在ICE-lite过程中,客户端不收集所有候选对象,而只收集本地host候选对象。这基本上是为位于公共IP地址后面的端点而设计的,当一个客户端位于一个没有NAT的公共IP后面时,它可以与任何其他候选端连接,即使另一端在对称NAT之后。ICE-Lite 不需要STUN/TURN服务器。您无法使用SDP来实现这一点,因为ICE-Lite过程在您获得候选对象之前首先出现。因此,如果你不设置STUN/TURN服务器,那么它将作为ICE-Lite工作(尽管它不是正式的ICE-Lite方式,ICE客户端应该有定义的方式来设置ICE-Full或ICE-Lite),因为现在它只收集候选主机。但如果您的端点在某个NAT之后,而另一个端点在网络之外,则它将无法工作。如果你能确定客户机是否在公共IP后面,那就更好了。