iOS_我们的对象会经历什么
原文出处:iOS_我们的对象会经历什么
文章是对最近一次技术分享 - 关于对象从创建到销毁的过程探究的整理.
@autoreleasepool
{
NSObject (__strong) *object = [[NSObject alloc]init];
}
全文探讨基本上是对上面这句代码的说明.
目录
一. NSObject
二. alloc
三. init
四. 所有权修饰符
五. autoreleasepool
六. dealloc
一. NSObject
1. NSObject内存结构
由于内存分配会涉及到对象的结构,因此首先对对象的结构加以说明,如图:
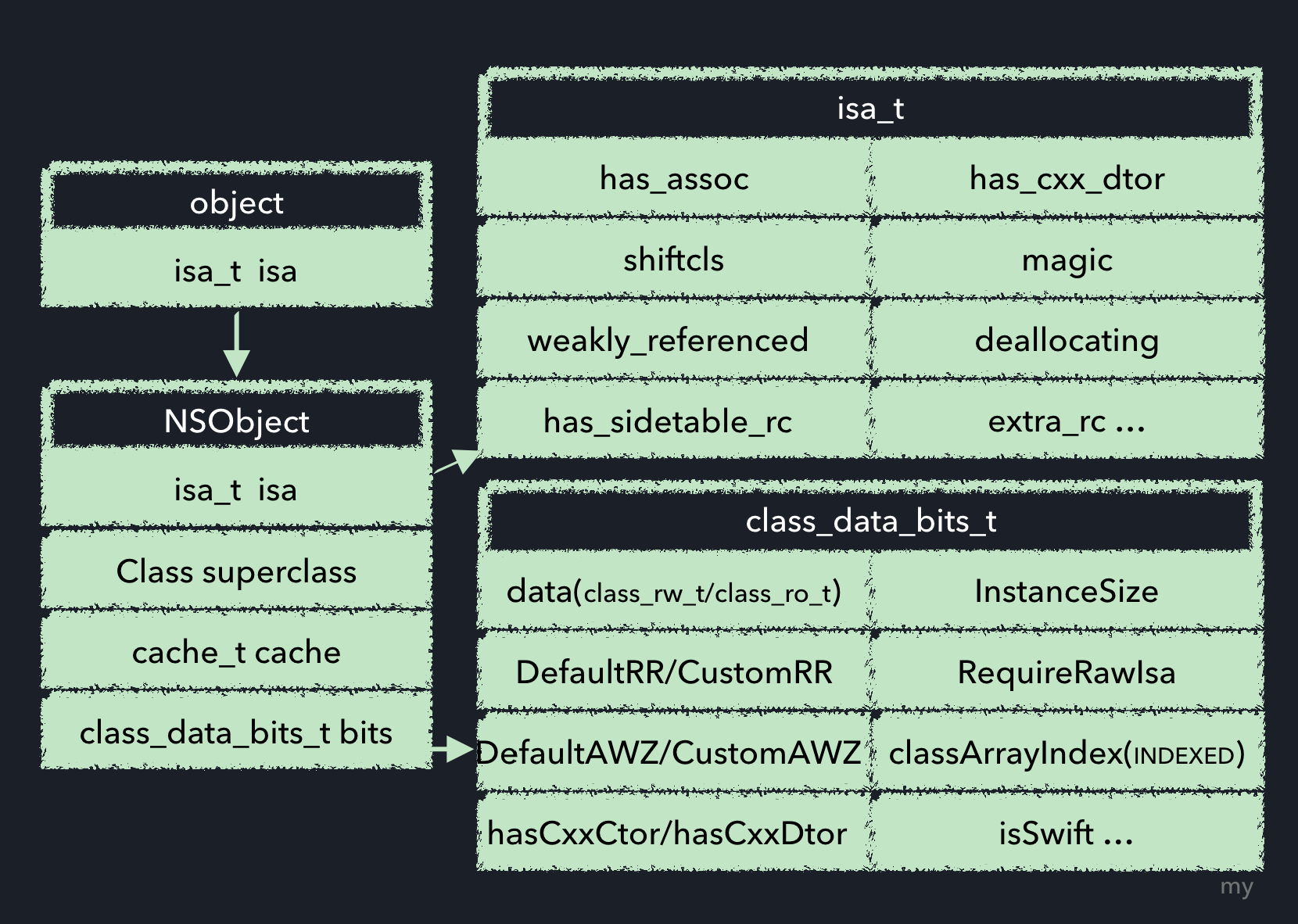
NSObject结构图
实例对象的isa指针指向类对象.而根据runtime源码,我们可以看到类objc_class是继承自objc_object的,本质上,类是一个对象,这也就是我们通常会说的'类对象'的缘由.
其中objc_object有一个唯一的私有变量 - isa_t类型的isa指针,objc_class的定义中还包括了:
Class superclass- 指向父类;cache_t cache- 方法缓存,具体可参考这篇文章:深入理解Objective-C:方法缓存;class_data_bits_t bits- 存储类方法,属性,遵从协议等数据.
2. isa_t isa
union isa_t
{
isa_t() { }
isa_t(uintptr_t value) : bits(value) { }
Class cls;
uintptr_t bits;
##if __arm64__
#### define ISA_MASK 0x0000000ffffffff8ULL
#### define ISA_MAGIC_MASK 0x000003f000000001ULL
#### define ISA_MAGIC_VALUE 0x000001a000000001ULL
struct {
uintptr_t nonpointer : 1;
uintptr_t has_assoc : 1;//对象含有或者曾经含有关联引用,没有关联引用的可以更快地释放内存
uintptr_t has_cxx_dtor : 1;//析构器方法,如果没有析构器就会快速释放内存
uintptr_t shiftcls : 33; // MACH_VM_MAX_ADDRESS 0x1000000000
uintptr_t magic : 6;//用于调试器判断当前对象是真的对象还是没有初始化的空间
uintptr_t weakly_referenced : 1;//对象被指向或者曾经指向一个 ARC 的弱变量,没有弱引用的对象可以更快释放
uintptr_t deallocating : 1;//对象正在释放内存
uintptr_t has_sidetable_rc : 1;//对象的引用计数太大了,存不下
uintptr_t extra_rc : 19;//对象的引用计数超过 1,会存在这个这个里面
#### define RC_ONE (1ULL<<45)
#### define RC_HALF (1ULL<<18)
};
##elif __x86_64__
#### define ISA_MASK 0x00007ffffffffff8ULL
#### define ISA_MAGIC_MASK 0x001f800000000001ULL
#### define ISA_MAGIC_VALUE 0x001d800000000001ULL
struct {
uintptr_t nonpointer : 1;
uintptr_t has_assoc : 1;
uintptr_t has_cxx_dtor : 1;
uintptr_t shiftcls : 44; // MACH_VM_MAX_ADDRESS 0x7fffffe00000
uintptr_t magic : 6;
uintptr_t weakly_referenced : 1;
uintptr_t deallocating : 1;
uintptr_t has_sidetable_rc : 1;
uintptr_t extra_rc : 8;
#### define RC_ONE (1ULL<<56)
#### define RC_HALF (1ULL<<7)
};
##else
#### error unknown architecture for packed isa
##endif
// SUPPORT_PACKED_ISA
#endif
#if SUPPORT_INDEXED_ISA
##if __ARM_ARCH_7K__ >= 2
#### define ISA_INDEX_IS_NPI 1
#### define ISA_INDEX_MASK 0x0001FFFC
#### define ISA_INDEX_SHIFT 2
#### define ISA_INDEX_BITS 15
#### define ISA_INDEX_COUNT (1 << ISA_INDEX_BITS)
#### define ISA_INDEX_MAGIC_MASK 0x001E0001
#### define ISA_INDEX_MAGIC_VALUE 0x001C0001
struct {
uintptr_t nonpointer : 1;
uintptr_t has_assoc : 1;
uintptr_t indexcls : 15;
uintptr_t magic : 4;
uintptr_t has_cxx_dtor : 1;
uintptr_t weakly_referenced : 1;
uintptr_t deallocating : 1;
uintptr_t has_sidetable_rc : 1;
uintptr_t extra_rc : 7;
#### define RC_ONE (1ULL<<25)
#### define RC_HALF (1ULL<<6)
};
##else
#### error unknown architecture for indexed isa
##endif
// SUPPORT_INDEXED_ISA
#endif
};
以上为isa指针的定义,可以看到isa指针是一个联合体,在不同环境下,结构体中属性值稍有差别.
其中
SUPPORT_INDEXED_ISA,文档注释Define SUPPORT_INDEXED_ISA=1 on platforms that store the class in the isa field as an index into a class table.,也就是当该属性为真,则把该类存储在isa中,作为全局class表的索引();nonpointer为1,表示使用优化的isa指针,包含了引用计数,析构状态等.has_assoc,是否包含关联对象,如果没有,会更快的释放内存;has_cxx_dtor,是否包含析构函数,如果没有,会更快的释放内存;shiftcls,类的指针;magic,固定值,用于判断是否完成初始化;weakly_referenced,对象是否指向一个弱引用对象,没有弱引用对象可以更快的被释放;deallocating,对象是否正在销毁;has_sidetable_rc,是否有sidetable(散列表),如果为真,则引用计数存储在该散列表中;extra_rc,存储引用计数,比真实的引用计数少1.
散列表,引用计数等具体的说明,文章后面部分做简单介绍.
3. class_data_bits_t bits
限于篇幅,不再展示完整的定义(objc4-706,objc-runtime-new.h文件,844-1056行),可参考前文图示,标识了几个主要属性.
由源码可知,类结构中bits属性是一个叫做class_data_bits_t的结构体,包含Bits相关的set,get与clear私有属性,和data等相关的公开属性,下面对公开属性做简单说明:
class_rw_t* data,存储该类方法属性协议等相关内容的指针,该结构体包含一个const class_ro_t *ro只读属性ro,ro中存储类在编译阶段就存在的方法属性协议等,因此当在运行时向类添加方法,那么改变的是class_rw_t类型的rw中的方法列表,而不是class_ro_t类型的ro的列表(rw即读写,ro即只读).hasDefaultRR,当前类或者父类是否含有默认的retain/release/autorelease/retainCount/_tryRetain/_isDeallocating/retainWeakReference/allowsWeakReference方法;hasDefaultAWZ,当前类或者父类是否含有allocWithZone方法;hasCxxCtor,是否有构造方法,alloc时使用;hasCxxDtor,是否有析构方法,dealloc时使用;instancesRequireRawIsa,是否需要RawIsa(?)的标识;fastInstanceSize,实例大小;classArrayIndex,索引,当SUPPORT_INDEXED_ISA为假时,值为0;isSwift,是否使用的是Swift语言;
二. alloc
1.alloc流程
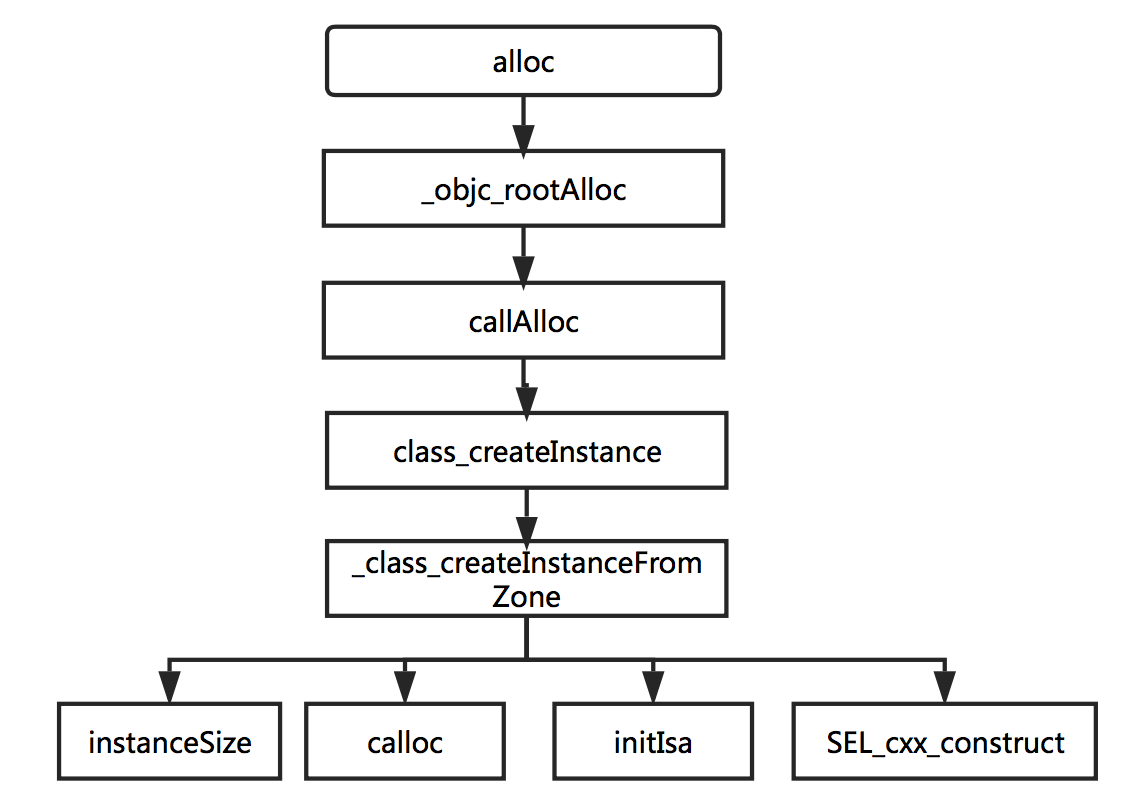
alloc简化调用堆栈
alloc方法完整的执行过程包括非常多的判断和跳转,这里做了简化.
当我们写了一个[Class alloc]命令,会相应的调用_objc_rootAlloc方法,最终会执行_class_createInstanceFromZone方法,如下:
static __attribute__((always_inline))
id
_class_createInstanceFromZone(Class cls, size_t extraBytes, void *zone,
bool cxxConstruct = true,
size_t *outAllocatedSize = nil)
{
if (!cls) return nil;
assert(cls->isRealized());
//1. Read class's info bits all at once for performance
bool hasCxxCtor = cls->hasCxxCtor();
bool hasCxxDtor = cls->hasCxxDtor();
bool fast = cls->canAllocNonpointer();
//2.
size_t size = cls->instanceSize(extraBytes);
if (outAllocatedSize) *outAllocatedSize = size;
//3.
id obj;
if (!zone && fast) {
obj = (id)calloc(1, size);
if (!obj) return nil;
obj->initInstanceIsa(cls, hasCxxDtor);
}
else {
if (zone) {
obj = (id)malloc_zone_calloc ((malloc_zone_t *)zone, 1, size);
} else {
obj = (id)calloc(1, size);
}
if (!obj) return nil;
// Use raw pointer isa on the assumption that they might be
// doing something weird with the zone or RR.
obj->initIsa(cls);
}
//4.
if (cxxConstruct && hasCxxCtor) {
obj = _objc_constructOrFree(obj, cls);
}
return obj;
}
- 1.这部分是读取类的基本信息,上文类结构中已做说明.
- 2.我们看到这里的size,也就是获取对象的内存大小,继续查看
instanceSize,找到如下内容:
uint32_t unalignedInstanceSize() {
assert(isRealized());
return data()->ro->instanceSize;
}
uint32_t alignedInstanceSize() {
return word_align(unalignedInstanceSize());
}
size_t instanceSize(size_t extraBytes) {
size_t size = alignedInstanceSize() + extraBytes;
if (size < 16) size = 16;
return size;
}
也就是说会在类的ro属性instanceSize中读取,然后经过对齐后返回.
这里要补充的有两点:
1). 对象的内存地址和大小是在编译阶段就确定了的,编译阶段存在的内容会存储在类结构data中,而此时访问data,则为ro,在运行时,系统会将ro中的
数据赋值到rw中,并重新设置对象的内存结构,此时访问data,则为rw.
2). ' CF requires all objects be at least 16 bytes.'
所有的对象的大小都必须大于或等于 16 字节。
3.在第2步获取了内存的大小之后,紧接着便调用
calloc方法为对象分配内存空间.然后通过initInstanceIsa最终调用initIsa方法初始化isa指针.hasCxxCtor我们上文提到过,表示有构造方法.接着往下看:
id _objc_constructOrFree(id bytes, Class cls)
{
assert(cls->hasCxxCtor()); // for performance, not correctness
id obj = object_cxxConstructFromClass(bytes, cls);
if (!obj) free(bytes);
return obj;
}
id
object_cxxConstructFromClass(id obj, Class cls)
{
assert(cls->hasCxxCtor());
id (*ctor)(id);
Class supercls;
supercls = cls->superclass;
// 1 调用父类构造方法
if (supercls && supercls->hasCxxCtor()) {
bool ok = object_cxxConstructFromClass(obj, supercls);
if (!ok) return nil;
}
//2 调用自身构造方法
ctor = (id(*)(id))lookupMethodInClassAndLoadCache(cls, SEL_cxx_construct);
if (ctor == (id(*)(id))_objc_msgForward_impcache) return obj;
if ((*ctor)(obj)) return obj;
//3 失败,清理
if (supercls) object_cxxDestructFromClass(obj, supercls);
return nil;
}
简单来说,如果当前对象存在构造方法,则会依次调用父类和自身的构造方法,成功后返回对象,如果失败,则调用父类的析构方法来清理并返回nil.
这里提到的构造函数便是SEL_cxx_construct.至于该方法具体是什么,我们稍后再提.
Note
另外,要提醒大家使用Xcode自动跳转时要仔细一点,在runtime源码中有非常多的文件涉及到old版本和new版本.我在再次查阅过程中才意识到之前被引导到
old版本,这个部分内容之前存在非常多问题..觉得脸好疼..
希望大家不要犯同样的错误.
2. malloc
这个小节属于扩展,不了解也没关系.
上一部分我们提到了calloc方法,而该方法会最终走到libsystem_malloc.dylib的malloc方法来分配内存.
这里做以简单说明,更多内容可参考这篇文章.
malloc内存分配基于malloc zone,并将基于大小分为nano、tiny、small、large四种类型,申请时按需分配.具体信息如下图:
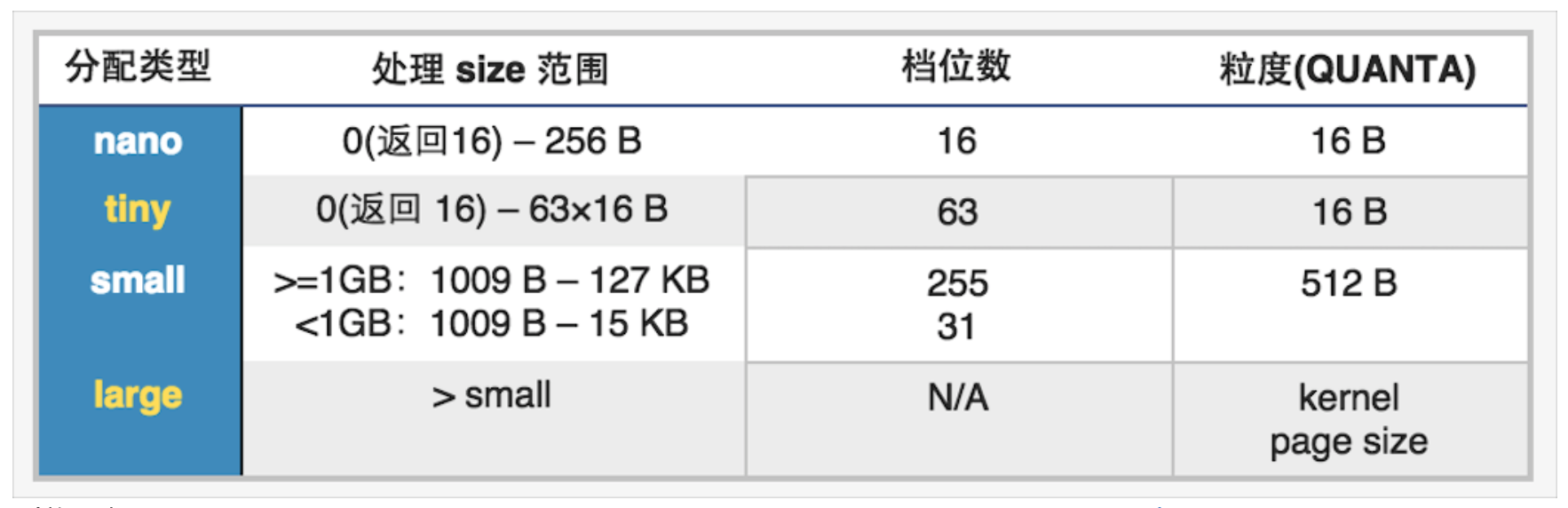
malloc zone
malloc在初次调用时,会分配一个default zone和一个scalable zone作为辅助,在64位环境下,default zone为nano zone,负责分配nano大小,scalable zone负责tiny、small和large内存的分配.
三. init
- (id)init {
return _objc_rootInit(self);
}
id
_objc_rootInit(id obj)
{
return obj;
}
init方法就简单了,只是返回当前对象,并没有其他多余操作.
2.16 补充
在巧哥的谈ObjC对象的两段构造模式这篇文章中提到:
"当我们通过 alloc 或 allocWithZone 方法创建对象时,cocoa 会返回一个未” 初使化 “过的对象。在这个过程中,cocoa除了上面提到的申请了一块足够大的内存外,还做了以下 3 件事:
将该新对象的引用计数 (Retain Count) 设置成 1。
将该新对象的 isa 成员变量指向它的类对象。
将该新对象的所有其它成员变量的值设置成零。(根据成员变量类型,零有可能是指 nil 或 Nil 或 0.0)"
但是这篇文章发表于2013-01-13,所以我觉得这部分内容可能已经不适用了,但是可以帮助我们了解alloc与init两段构造模式是由于历史原因以及Single Responsibility设计原则.
四. 所有权修饰符
该部分通过product -> Perform Action ->
Assemble追踪,因为对汇编代码知之甚少,只观察内存管理相关关键词(扶额.png)..
1. __strong
1.1 对象持有自己
利用alloc/new/copy/mutableCopy生成对象,此处以alloc为例:
NSDictionary *dic = [[NSDictionary alloc]init];
我们声明了一个dic对象,相应的会调用:
id dic = objc_msgSend(NSDictionary, @selector(alloc));
objc_msgSend(obj,selector(init));
objc_storeStrong(dic);
也就是在ARC环境下,自动插入_objc_storeStrong命令,那么这个命令做了什么呢?
void
objc_storeStrong(id *location, id obj)
{
id prev = *location;
if (obj == prev) {
return;
}
objc_retain(obj);
*location = obj;
objc_release(prev);
}
也就是在值发生变化时,retain新值,并release旧值.
1.2 对象不持有自己
利用非alloc/new/copy/mutableCopy生成对象,如下:
NSDictionary *dic = [NSDictionary dictionary];
相应的会调用
id dic = objc_msgSend(NSDictionary, @selector(dictionary));
objc_objc_retainAutoreleasedReturnValue(dic);
objc_storeStrong(dic);
在非持有关系中,除了objc_storeStrong命令,还多了一个objc_objc_retainAutoreleasedReturnValue,
objc_objc_retainAutoreleasedReturnValue是autoreleasepool的一个内存优化命令,后面autore
leasepool部分具体说明.
2. __weak
__weak通常用来解决循环引用的问题.如下示例代码:
id __weak obj1 = obj;
相应的会调用:
id obj ;
objc_initWeak(&obj1,obj);
objc_destoryWeak(&obj1);
在runtime源码中查看,会发现 objc_initWeak和objc_initWeak都是对objc_storeWeak函数的封装,那么
objc_storeWeak都做了什么呢?做了简化后如下:
storeWeak(id *location, objc_object *newObj)
{
SideTable *oldTable;
SideTable *newTable;
...
if (HaveOld)
{
weak_unregister_no_lock(&oldTable->weak_table, oldObj, location);
}
if (HaveNew)
{
newObj = (objc_object *)weak_register_no_lock(&newTable->weak_table,
(id)newObj, location,
CrashIfDeallocating);
*location = (id)newObj;
}
忽略掉繁琐的操作后,也就是清除旧值,并设置新值.
另外,我们注意到这里的SideTable和weak_table.这两个就是存储弱引用的表了,那么具体呢?

SideTable结构图
如图,SideTable是一个散列表,包含三个属性:
spinlock_t shock,锁,保证操作安全;RefcountMap refcnts,引用计数表,存储当前对象的引用计数;weak_table_t weak_table,也就是我们刚提到的weak_table.weak_table含有一个属性weak_entry_t *weak_entries,它负责维护和存储指向一个对象的所有弱引用hash表,weak_entry_t本身也是一个结构体,其定义如下:
struct weak_entry_t {
DisguisedPtr<objc_object> referent;//被引用的对象
union {
struct {
weak_referrer_t *referrers;//The address of a __weak variable.
uintptr_t out_of_line_ness : 2;
uintptr_t num_refs : PTR_MINUS_2;
uintptr_t mask;
uintptr_t max_hash_displacement;
};
struct {
// out_of_line_ness field is low bits of inline_referrers[1]
weak_referrer_t inline_referrers[WEAK_INLINE_COUNT];//4
};
};
bool out_of_line() {
return (out_of_line_ness == REFERRERS_OUT_OF_LINE);
}
weak_entry_t& operator=(const weak_entry_t& other) {
memcpy(this, &other, sizeof(other));
return *this;
}
weak_entry_t(objc_object *newReferent, objc_object **newReferrer)
: referent(newReferent)
{
inline_referrers[0] = newReferrer;
for (int i = 1; i < WEAK_INLINE_COUNT; i++) {
inline_referrers[i] = nil;
}
}
};
其中referent是被引用对象(key),也就是示例代码中的obj,下面的union即存储了所有指向该对象的弱引用,其中referrers
存储所有的弱引用对象的地址(value),且当引用少于4时,hash表被一个数组所代替。
在hash表中,赋值对象的内存地址作为键值key,第一个参数__weak修饰的属性变量的内存地址作为value存储.
具体来说,初始化时,objc_initWeak(&obj1,obj)将执行objc_storeWeak(&obj1, obj);,将被引用对象ob
j地址作为key值,将当前引用对象obj1作为value存储,而当obj引用计数为0时,objc_destoryWeak(&obj1)函数会执
行objc_storeWeak(&obj1,0),把变量obj1的地址从 weak 表中删除.
涉及到SideTable,那么我们可以顺便了解一下retain release 与retainCount了.
retain
retain操作实现如下:
id objc_object::sidetable_retain()
{
#if SUPPORT_NONPOINTER_ISA
assert(!isa.nonpointer);
#endif
SideTable& table = SideTables()[this];
table.lock();
size_t& refcntStorage = table.refcnts[this];
if (! (refcntStorage & SIDE_TABLE_RC_PINNED)) {
refcntStorage += SIDE_TABLE_RC_ONE;
}
table.unlock();
return (id)this;
}
可以看到,retain操作是读取当前对象的SideTable中refcnts属性,如果没有越界,会将其增加SIDE_TABLE_RC_ONE
即(1UL<<2),而不仅仅是我们熟知的1,这由于引用计数的第一位用来表示计数是否越界,后两位分别被弱引用以及析构状态两个标识位占领.
retainCount
在说release之前,先说一下retainCount的实现.
#define SIDE_TABLE_RC_SHIFT 2
uintptr_t objc_object::sidetable_retainCount()
{
SideTable& table = SideTables()[this];
size_t refcnt_result = 1;
table.lock();
RefcountMap::iterator it = table.refcnts.find(this);
if (it != table.refcnts.end()) {
// this is valid for SIDE_TABLE_RC_PINNED too
refcnt_result += it->second >> SIDE_TABLE_RC_SHIFT;
}
table.unlock();
return refcnt_result;
}
sidetable_retainCount()函数的实现,印证了对象的引用计数存在在SideTable中的想法,而且引用计数总是返回1+table.refcnts.这也是为什么我们有时候会听到有人说访问到的引用计数不正确.
release
#define SIDE_TABLE_DEALLOCATING (1UL<<1) // MSB-ward of weak bit
#define SIDE_TABLE_RC_ONE (1UL<<2) // MSB-ward of deallocating bit
#define SIDE_TABLE_RC_PINNED (1UL<<(WORD_BITS-1))
uintptr_t objc_object::sidetable_release(bool performDealloc)
{
#if SUPPORT_NONPOINTER_ISA
assert(!isa.nonpointer);
#endif
SideTable& table = SideTables()[this];
bool do_dealloc = false;
table.lock();
RefcountMap::iterator it = table.refcnts.find(this);
if (it == table.refcnts.end()) {
do_dealloc = true;
table.refcnts[this] = SIDE_TABLE_DEALLOCATING;
} else if (it->second < SIDE_TABLE_DEALLOCATING) {
// SIDE_TABLE_DEALLOCATING 可作为计数是否为0的判断
do_dealloc = true;
it->second |= SIDE_TABLE_DEALLOCATING;
} else if (! (it->second & SIDE_TABLE_RC_PINNED)) {
it->second -= SIDE_TABLE_RC_ONE;
}
table.unlock();
if (do_dealloc && performDealloc) {
((void(*)(objc_object *, SEL))objc_msgSend)(this, SEL_dealloc);
}
return do_dealloc;
}
release操作,首先读取当前对象SideTable中refcnts属性,然后对计数加以判断,分类处理:
当引用计数为计数表中的最后一个,标记对象为正在析构
SIDE_TABLE_DEALLOCATING状态,然后执行完成后发送SEL_dealloc消息释放对象.关于dealloc过程,后文再提及.当计数表的值小于
SIDE_TABLE_DEALLOCATING,也就是小于1,为0 - 根据对sidetable_retainCount分析,我们知道即使refcnts也就是这里的it为0, 此时retainCount并不为0而是返回1.在这种情况下,也不进行减少计数的操作,而是直接标记对象正在析构SIDE_TABLE_DEALLOCATING.除此之外,则计数直接减去
SIDE_TABLE_RC_ONE,也就是(1UL<<2).
3. unsafe_unretained
现在已经很少显式声明unsafe_unretained属性的变量,但值得注意的是,在ARC环境下,self并不会被retain和release,它其实是unsafe_unretained,生命周期全由它的调用方来保证.

clang文档关于self的说明
关于这一点,在苹果clang文档中有说明,另外也可以参考孙源的这篇文章.
4. _autoreleasing
_autoreleasing属性,是将对象放入autoreleaspool中,会在以下几种case出现:
- 方法参数(self除外)
- 方法返回值(init方法除外)
其中,当调用方给方法参数传递参数时,默认是strong类型,而接收方方法的参数是_autoreleasing,为什么没有出现类型不匹配错误呢? 这是因为系统自动插入了临时转换命令,将调用方的strong对象参数转换为_autoreleasing临时变量传递给接收方.而当参数是__weak类型时,也类似,会讲__weak变量转换为_autoreleasing作为入参.
而加入autoreleaspool,具体发生了什么呢?
五. autoreleasepool
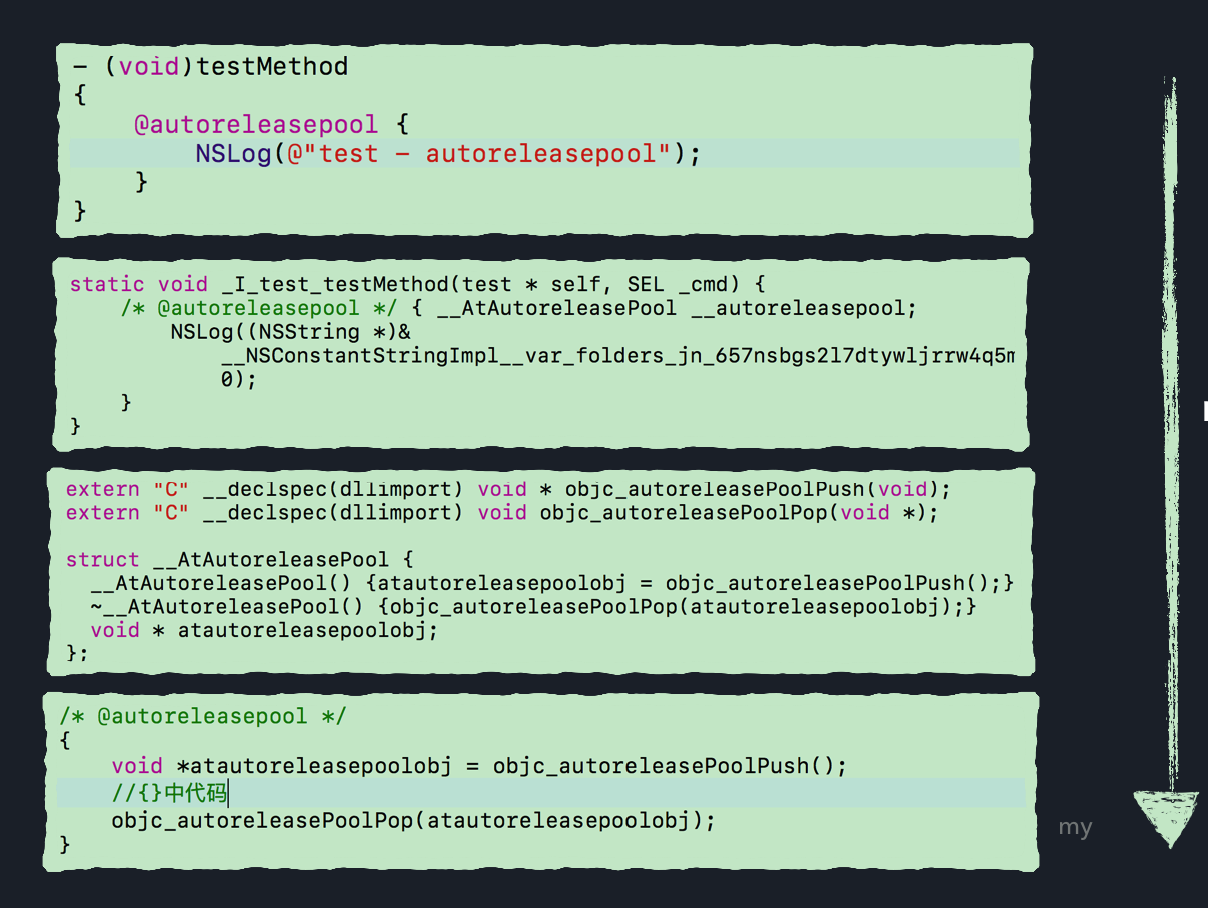
autoreleasepool追踪
通过clang重新文件之后,可以看到autoreleasepool被转换为两个命令objc_autoreleasePoolPush和objc_auto releasePoolPop,而查阅源码,会发现,这两个命令都是基于AutoreleasePoolPage的封装.
class AutoreleasePoolPage
{
...
magic_t const magic;//用来校验AutoreleasePoolPage的结构是否完整
id *next;//游标,指向栈顶最新add进来的对象的下一个位置
pthread_t const thread;//当前线程, thread:pool = 1:n
AutoreleasePoolPage * const parent;//parent指针与child构成双向链表
AutoreleasePoolPage *child;//
uint32_t const depth;//深度
...
}
1. push
继续跟踪push方法,其流程如下:
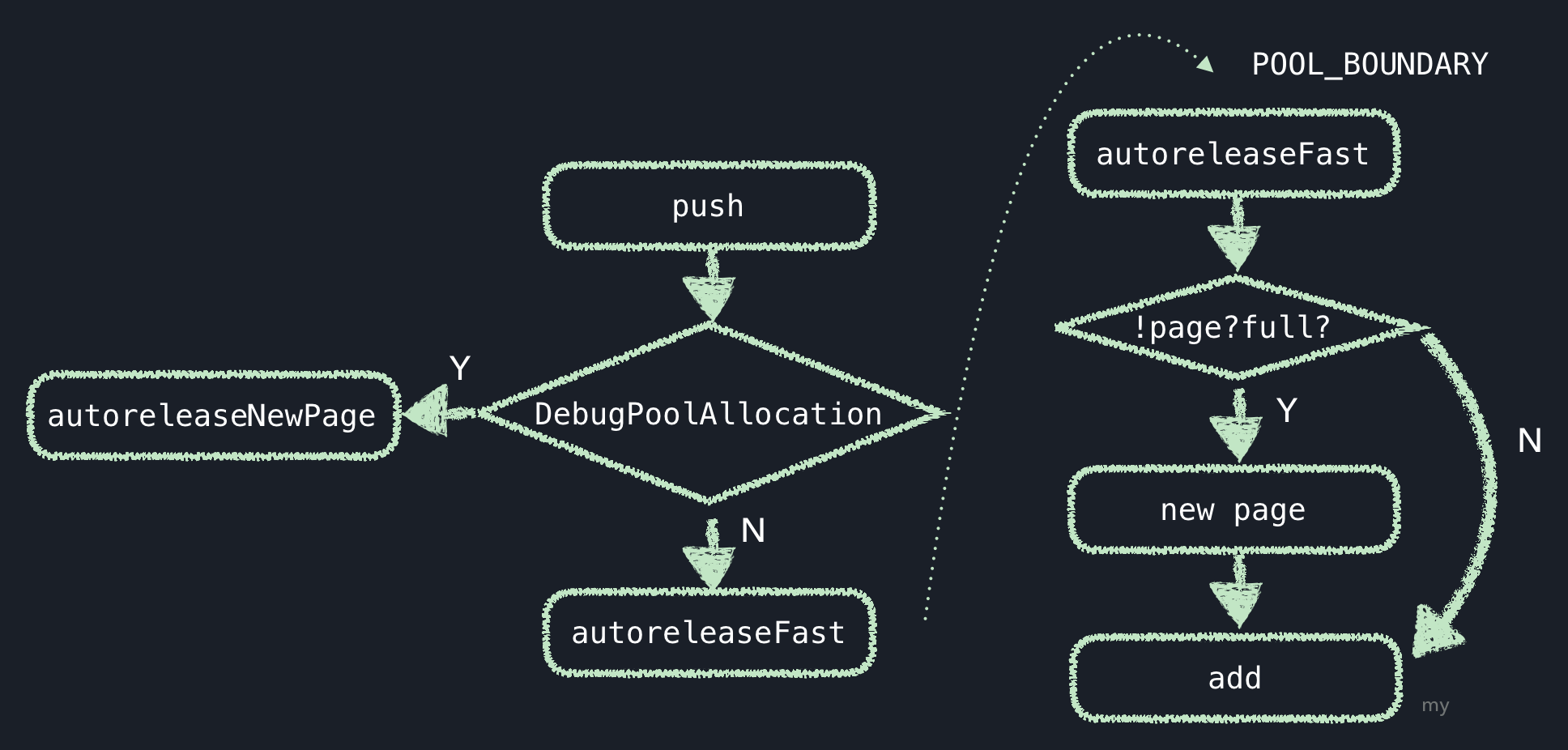
push - autoreleaseFast流程图
首先会判断类别,如果是需要每个pool都生成一个新page,即DebugPoolAllocation为真,则执行autoreleaseNewPage方法,否则,执行autoreleaseFast方法.
在autoreleaseFast方法中,如果存在page且未满,则直接添加;
如果不存在page,会响应autoreleaseNoPage;
如果当前page已满,则响应autoreleaseFullPage方法;
autoreleaseNoPage和autoreleaseFullPage会生成新的page,然后向该page中添加对象.
而autoreleaseNewPage方法,如果当前存在page,则执行autoreleaseFullPage方法,否则响应autorelea
seNoPage方法,然后就同上了,去执行添加方法.
具体如何添加呢?
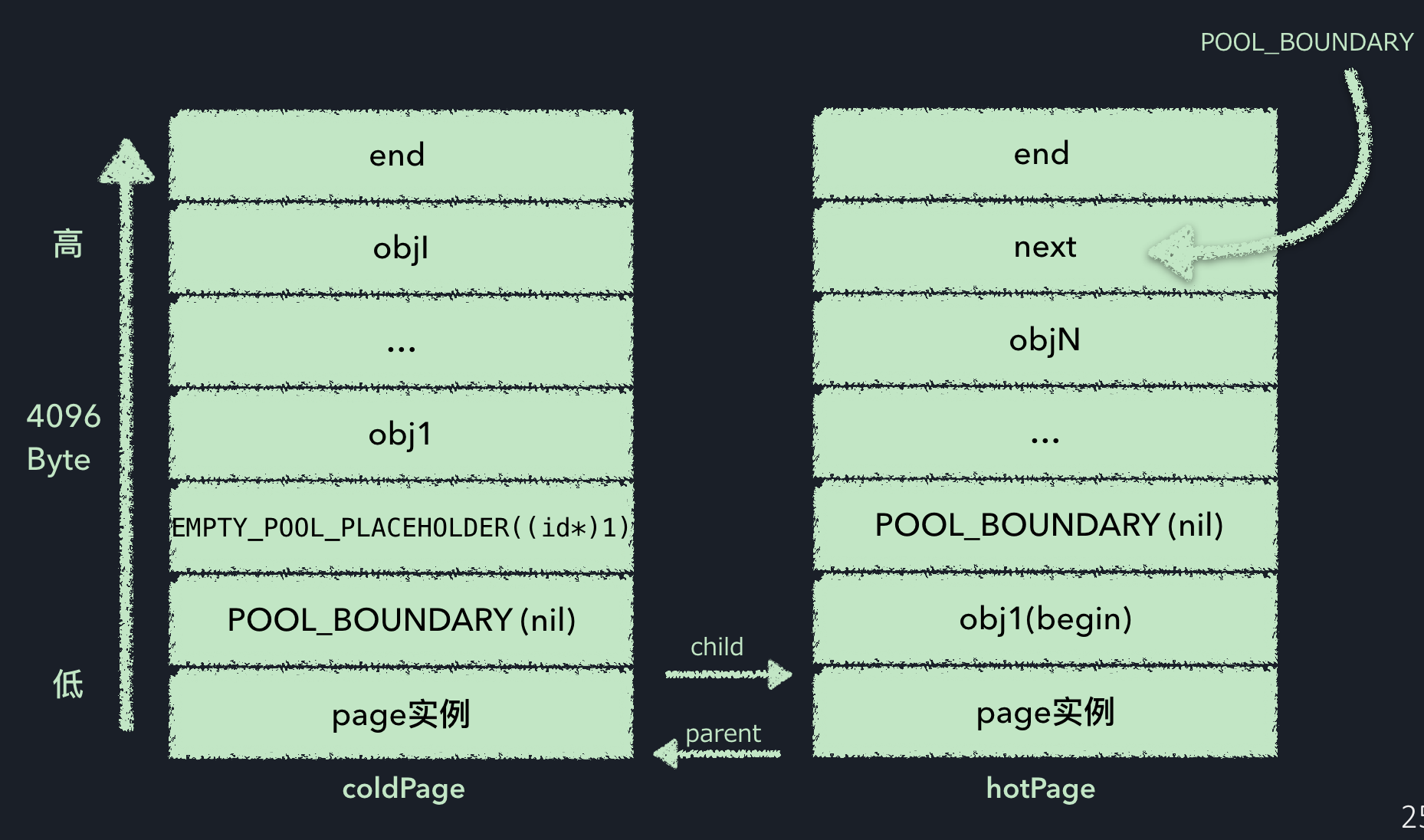
push add 示意图
在一个page中,除了存储page实例本身的数据空间,都用来存储加入pool的对象.
当插入对象时,会在next指针位置首先插入一个POOL_BOUNDARY对象(一个nil对象)作为标示,然后添加实例对象,并在末尾处更新next指针,使其指向下一个add进来的对象的位置,也就是下一个POOL_BOUNDARY对象了,然后返回插入哨兵对象的地址.
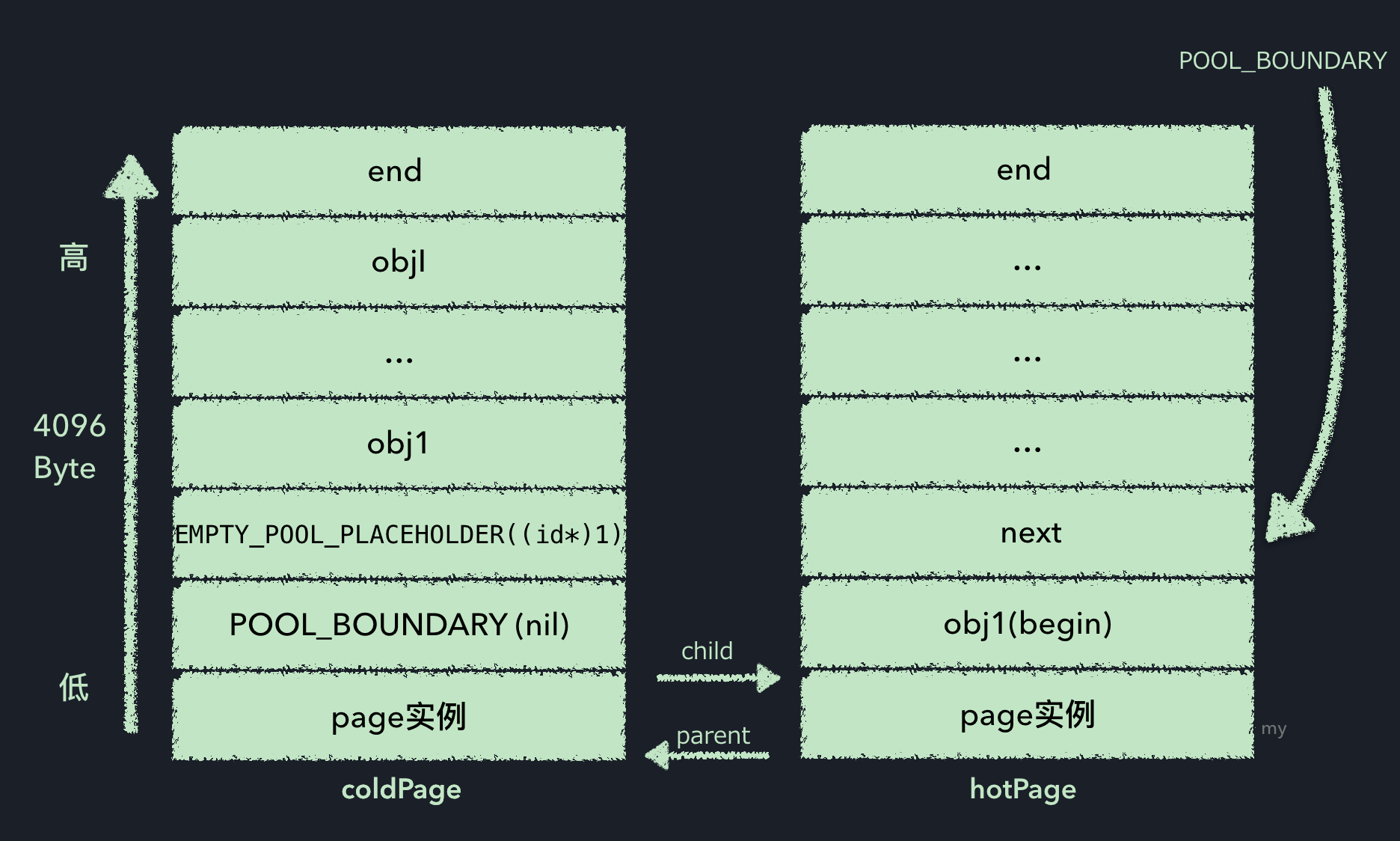
2. pop
收到pop命令后,首先会根据push操作返回的POOL_BOUNDARY哨兵对象的地址获取到当前page,然后在当前page中,将晚于哨兵对象添
加的对象都发送一次release命令,并更新next指针位置,最后kill掉空page,示意如下:
pop release示意图
一个曾经困扰我的问题是:
既然一个线程可以对应多个pool,而pool可以嵌套并且是可以跨page的,那么,当只需要销毁内层pool中的对象时,会发生什么呢?
这个问题在意识到,pool的销毁是在线程结束时发生的,因此即使有多个pool,也会在同一时间销毁,不存在只销毁内层的状态.???
3. TLS
在追踪push的时候,注意到源码中对EMPTY_POOL_PLACEHOLDER的一段注释:
// EMPTY_POOL_PLACEHOLDER is stored in TLS when exactly one pool is
// pushed and it has never contained any objects. This saves memory
// when the top level (i.e. libdispatch) pushes and pops pools but
// never uses them.
好奇这个TLS到底是个什么样的存在,做了一点功课.
TLS,Thread Local
Storage,线程局部存储,也就是将一块内存作为某个线程专属的存储,同一线程的多个pool共享这个存储区域.那么这个区域具体存储什么呢?
上文__strong的实现中我们提到,对于自己不持有的对象,系统会自动插入的一个命令objc_retainAutoreleasedReturnValue,与之对应的还有objc_retainAutoreleasedReturnValue
objc_autoreleaseReturnValue.更详细的优化命令如下图:
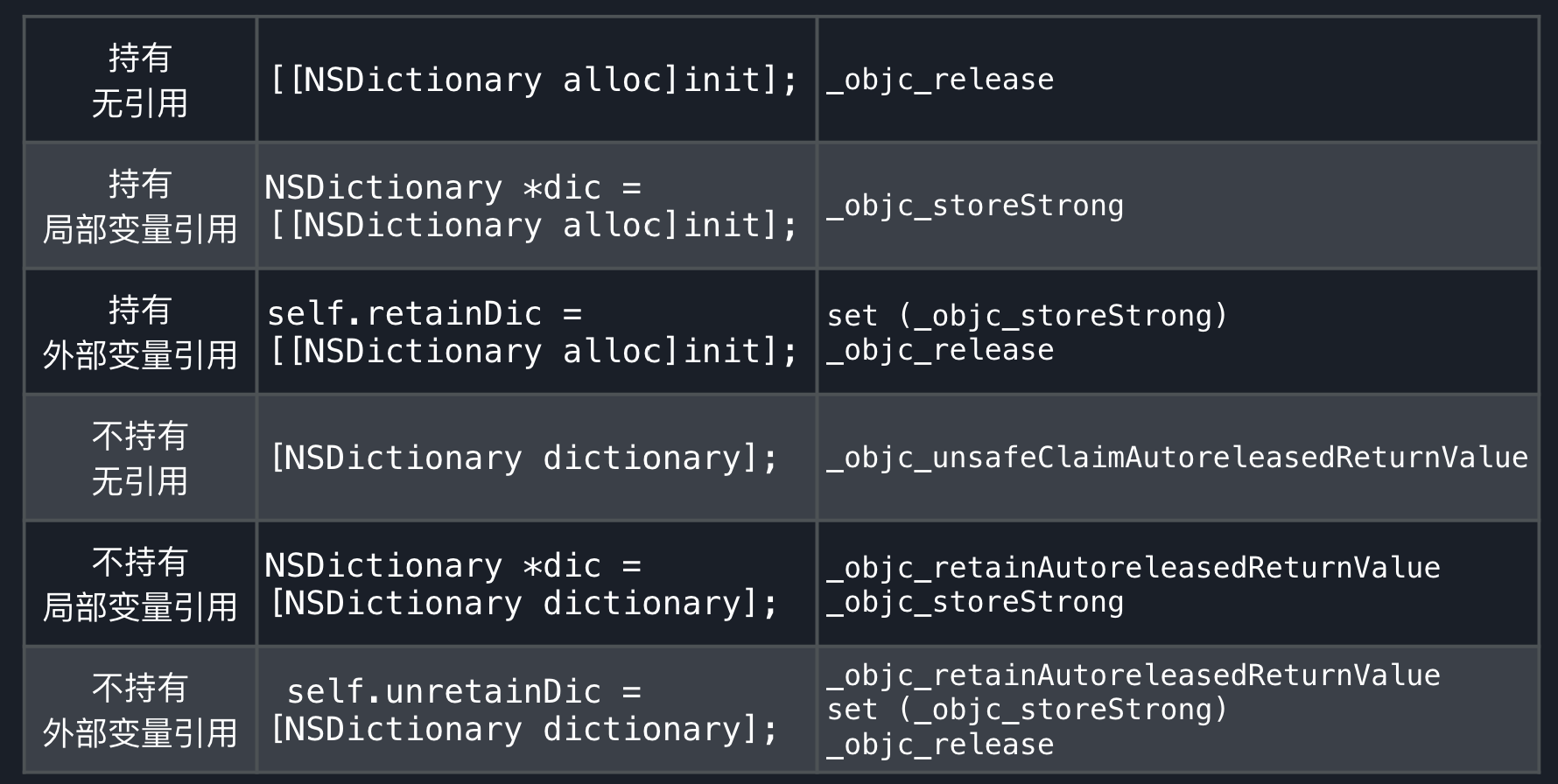
autorelease 进行的优化
那么这些命令和TLS又有什么关系呢?上代码:
id objc_retainAutoreleasedReturnValue(id obj)
{
if (acceptOptimizedReturn() == ReturnAtPlus1) return obj;
return objc_retain(obj);
}
id objc_autoreleaseReturnValue(id obj)
{
if (prepareOptimizedReturn(ReturnAtPlus1)) return obj;
return objc_autorelease(obj);
}
其中的acceptOptimizedReturn 和prepareOptimizedReturn是优化标识,而优化标识和优化对象就是存储在TLS上的.当可以优化时,直接从TLS上返回当前对象地址,而不执行retain与release操作.
比如对同一个对象进行retain操作后又进行release操作,那么这两个操作都不会执行.
而更具体的什么时候存储在TLS上,什么情况下进行优化,现在还存疑,不再细说.
4. when
什么时候会创建
autoreleasepool?- 线程启动
runloop后自动生成NSAutoreleasePool接受对象,当当前runloop迭代结束时,释放该pool. enumerateObjectUsingBlock:,系统在这类快速遍历方法中会自动添加autoreleasepool.
- 线程启动
什么时候需要手动创建
autoreleasepool?- 非UI框架
- 大量临时变量
- 辅助线程
六. dealloc
dealloc方法在最后一次release后被调用,但此时实例变量(Ivars)并未释放,父类的dealloc的方法将在子类dealloc方
法返回后自动调用.析构对象,并释放空间..具体流程如图:
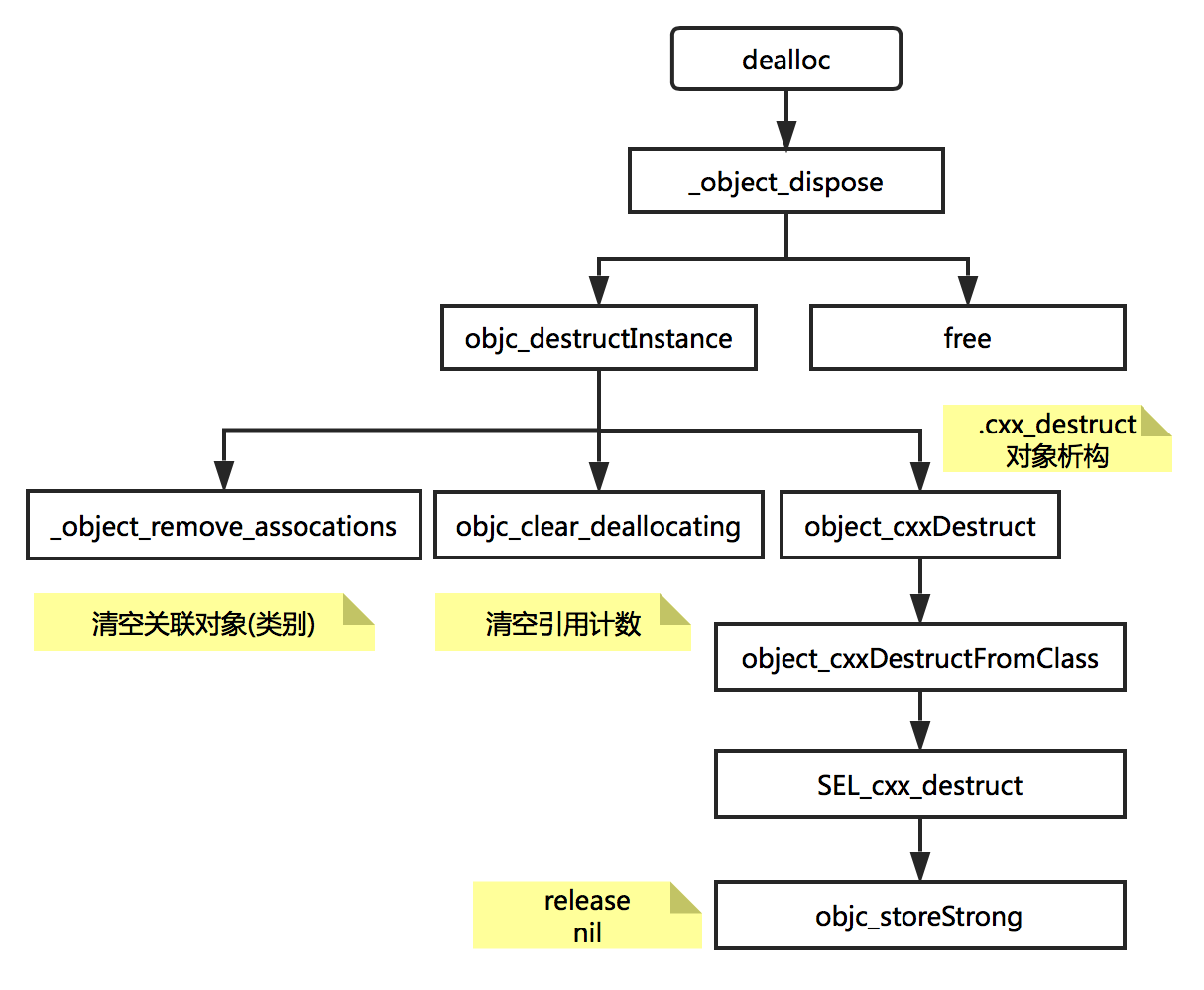
dealloc流程简图
其中,objc_clear_deallocating方法,除了清除SideTable中的引用计数外,也会对弱引用表进行清除.
这里提到的析构方法SEL_cxx_destruct,和上文提到的构造方法SEL_cxx_construct相对应.在孙源的ARC下dealloc过
程及.cxx_destruct的探究文
中提到SEL_cxx_destruct方法名为.cxx_destruct,而我在编号objc4-706的文件objc-
runtime.mm中只找到如下定义,不知道是不是版本不同已经更新的关系:
SEL SEL_cxx_construct = NULL;
SEL SEL_cxx_destruct = NULL;
七. 所以,这是所有了吗
不,还不是..
上面部分,我们大概梳理了对象的生成与销毁过程.那么什么时候生成该对象呢?在此之前发生了什么?
- 启动app之后,动态库从
start方法开始,完成动态库的加载; - 读取镜像文件,包括动态链接和可执行文件,类有了初始内存.
- 进入运行时初始化,将编译阶段的数据重新存储,更新类的内存结构.
- 调用所有类与分类的+load方法
- 进入main方法
- 某个条件触发,创建了该对象,初始化isa指针,为之分配了内存
- 对象去完成自己的使命,在此过程中引用计数发生变化,变化中系统会基于TLS做出优化,并在
SideTable中保存对象的引用计数和弱引用信息 - 最后调用dealloc方法,析构对象,释放内存,一切又归于平静了.

你知道我经历了什么
PS
一直在看,没有真正公开写过技术文,没想到...挺难的...
文章也不涉及新知识,没有什么高深见解,更多的只是梳理.虽然配图都是前期做PPT的时候画好的,但是还是用了一整天的时间才写到最后.知识有限,又难免被打断,也许
有疏漏错误之处,如果有人可以指出,会非常感激.
不管怎样,动手来写是个好的开始.
继续努力.